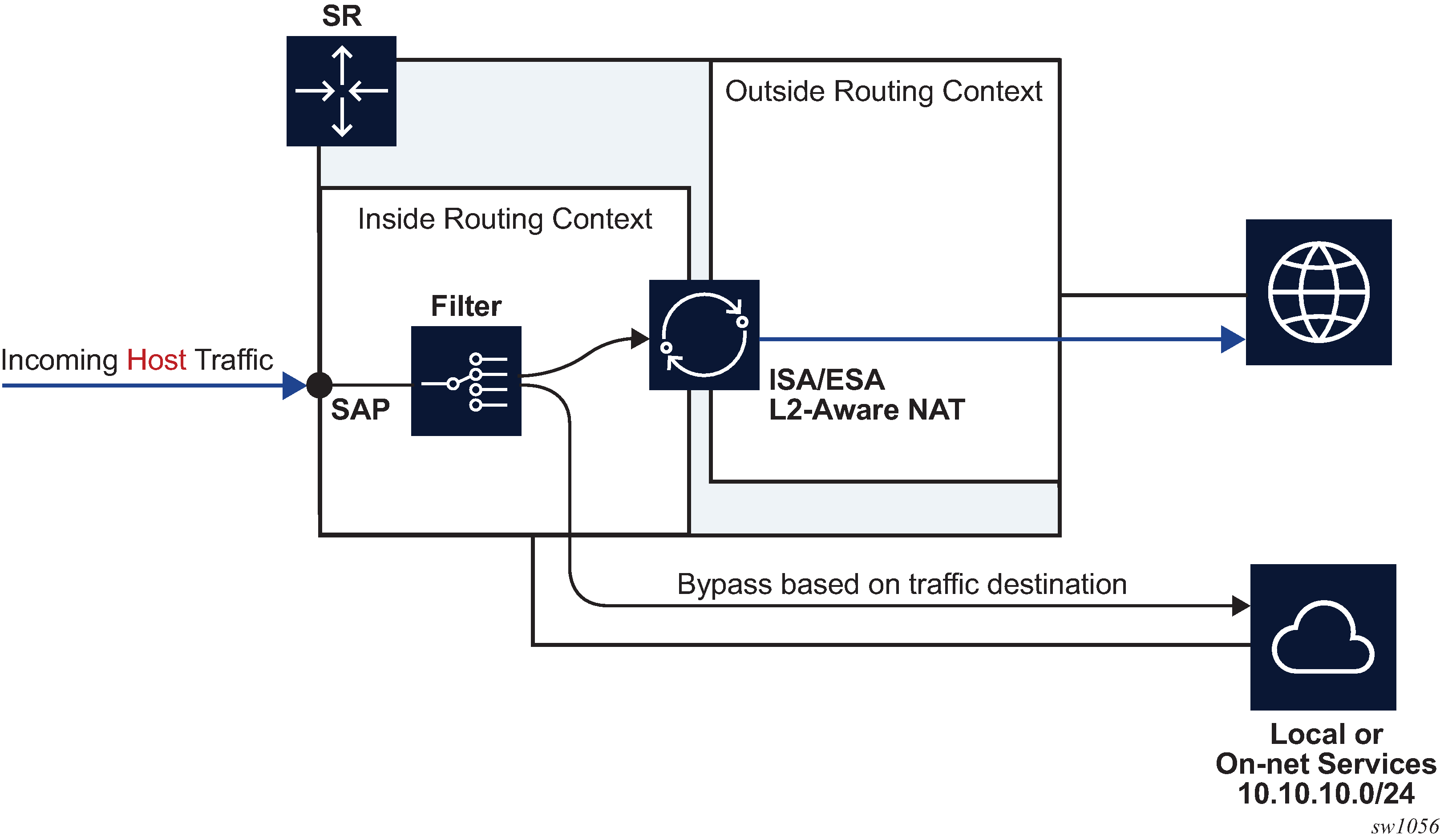
In selective L2-Aware NAT bypass, a decision whether to perform NAT is made based on the traffic classifiers (match conditions) defined in an IP filter applied to an ESM host.
A typical use case for selective L2-Aware NAT bypass is based on destinations, where on-net services are needed to be accessed without NAT, while some other off-net destinations, require NAT. Traffic to those on-net services is identified based on the destination IP addresses (Figure: L2-Aware bypass based on traffic destination).
L2-Aware NAT subscribers that are candidates for selective bypass in the SR OS, must be first identified and enabled with the config>subscr-mgmt>sub-prof>nat-allow-bypass command:
After the selective L2-Aware NAT bypass is enabled, the determination of whether specific traffic from a host bypasses NAT comes via an IP filter with a newly defined action l2-aware-nat-bypass. This new action must be configured in addition to the existing action accept (in MD-CLI) or forward (in classic CLI). This defined set of actions divert identified traffic away from NAT.
Although most typical use cases require traffic identification based on destination IP addresses, generic match statements in IP filters allow identification of traffic based on any Layer 3 fields.
The filter entries are executed in top-to-bottom order as shown in Figure: Filtering example for L2-Aware NAT bypass.
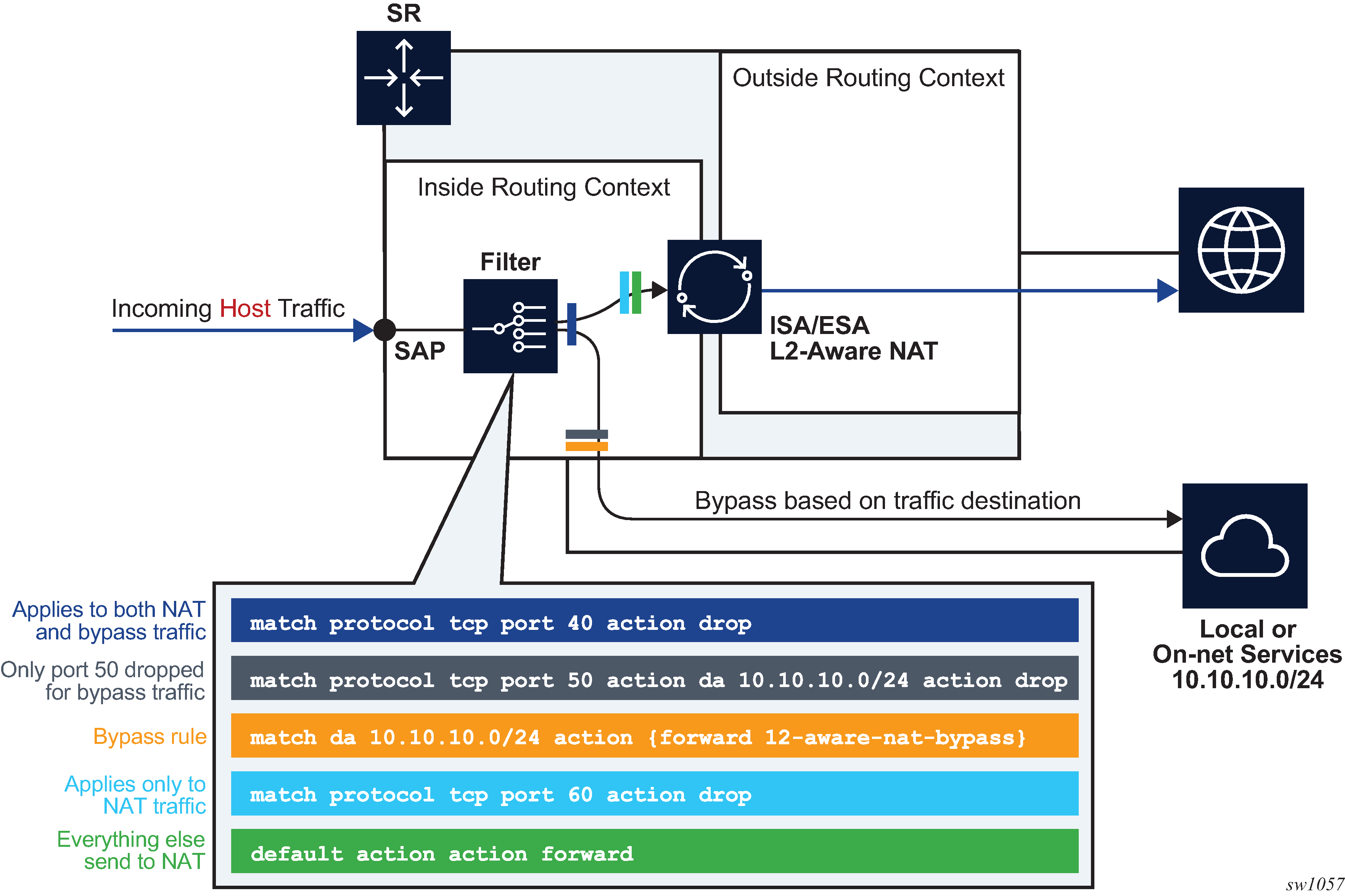
Table: Configuration options for selective L2-Aware NAT bypass describes the behavior in relation to the three configuration options that directly influence selective L2-Aware NAT bypass.
| L2-Aware NAT-enabled host | Selective bypass enabled | IP filter action l2-aware-nat-bypass accept | forward |
Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Selective bypass is in effect |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
The host is enabled for bypass, but without the corresponding IP filter action. Bypass is not in effect and all traffic from the host is NAT’d. After the bypass action is provided via the IP filter, traffic identified in the IP filter is bypassed. |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
The host is not enabled for bypass, but the IP filter is configured for bypass. This is an incorrect condition where host traffic is bypassed in the upstream direction but not in the downstream direction. As a result, downstream traffic is dropped. |
Yes |
No |
No |
The host is not enabled for bypass. All host traffic is NAT’d. |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
The host is not an L2-Aware NAT host. This is a full bypass case. |
No |
Yes |
No |
The host is not an L2-Aware NAT host. This is a full bypass case. |
No |
No |
Yes |
The host is not an L2-Aware NAT host. This is full bypass case. |
No |
No |
No |
The host is not an L2-Aware NAT host. This is full bypass case. |
The following are configuration considerations:
An ESM-enabled host can be enabled if the following two conditions are met:
The subscriber’s sub-profile contains the nat-policy name command.
The host IP address belongs to the subnet configured under the address command:
configure router/service vprn nat inside l2-aware address <ip-address/mask>
-
Selective bypass is enabled if the configure subscriber-mgmt sub-profile nat-allow-bypass command is configured under the sub-profile.
-
All configuration options are allowed in the CLI and it is up to the operator to consult Table: Configuration options for selective L2-Aware NAT bypass for expected results.