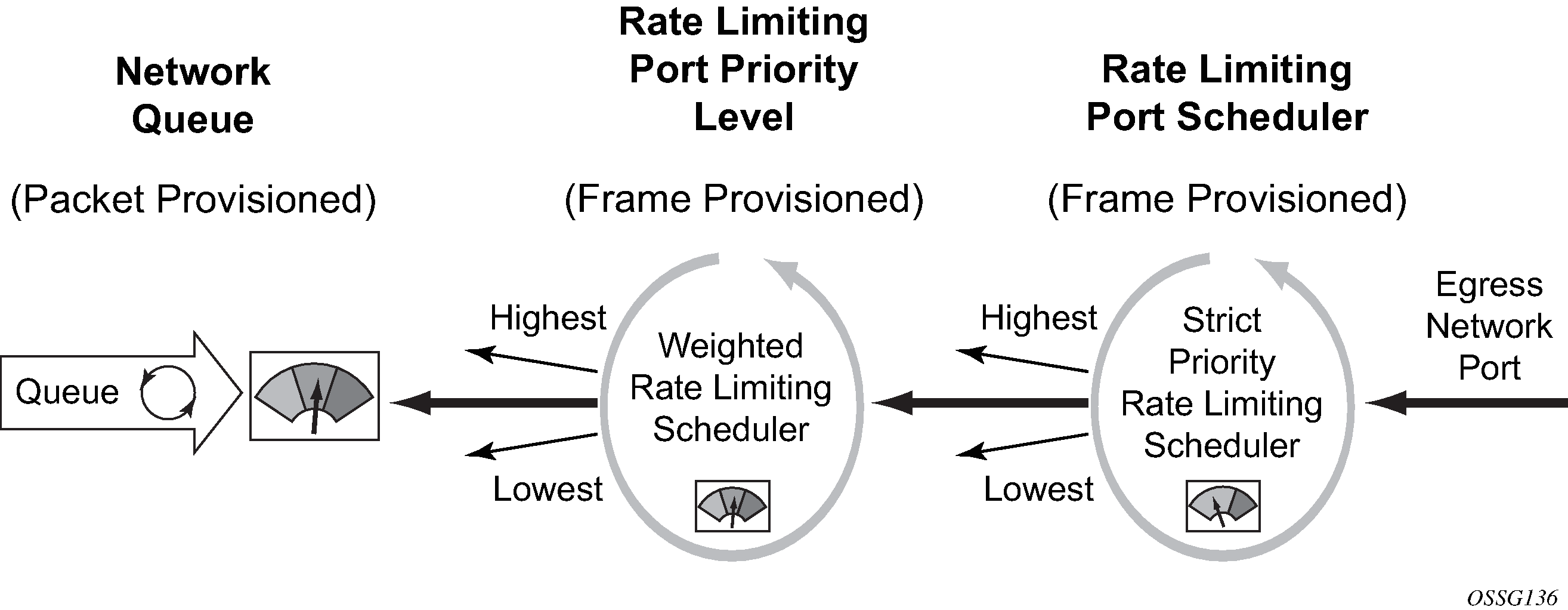
Network queues support port scheduler parent priority-level associations. Using a port scheduler policy definition and mapping network queues to a port parent priority level, H-QoS functionality is supported providing eight levels of strict priority and weights within the same priority. A network queue’s bandwidth is allocated using the within-CIR and above-CIR scheme normal for port schedulers.
Queue CIR and PIR percentages when port-based schedulers are in effect are based on frame-offered-load calculations. Figure: Bandwidth distribution on network port with port-based scheduling shows port-based virtual scheduling bandwidth distribution.
A network queue with a port parent association that exists on a port without a scheduler policy defined is considered to be orphaned.