The -SR OS implements IP routing functionality, providing support for IP version 4 (IPv4) and IP version 6 (IPv6). IP version 6 (RFC 1883, Internet Protocol, Version 6 (IPv6)) is a version of the Internet Protocol designed as a successor to IP version 4 (IPv4) (RFC-791, Internet Protocol). The changes from IPv4 to IPv6 affect the following categories:
expanded addressing capabilities
IPv6 increases the IP address size from 32 bits (IPv4) to 128 bits, to support more levels of addressing hierarchy, a much greater number of addressable nodes, and simpler auto-configuration of addresses. The scalability of multicast routing is improved by adding a scope field to multicast addresses. Also, a type of address called an anycast address is defined that is used to send a packet to any one of a group of nodes.
header format simplification
Some IPv4 header fields have been dropped or made optional to reduce the common-case processing cost of packet handling and to limit the bandwidth cost of the IPv6 header.
improved support for extensions and options
Changes in the way IP header options are encoded allows for more efficient forwarding, less stringent limits on the length of options, and greater flexibility for introducing options in the future.
flow labeling capability
The capability to enable the labeling of packets belonging to traffic flows for which the sender requests special handling, such as non-default quality of service or ‟real-time” service was added in IPv6.
authentication and privacy capabilities
Extensions to support authentication, data integrity, and (optional) data confidentiality are specified for IPv6.
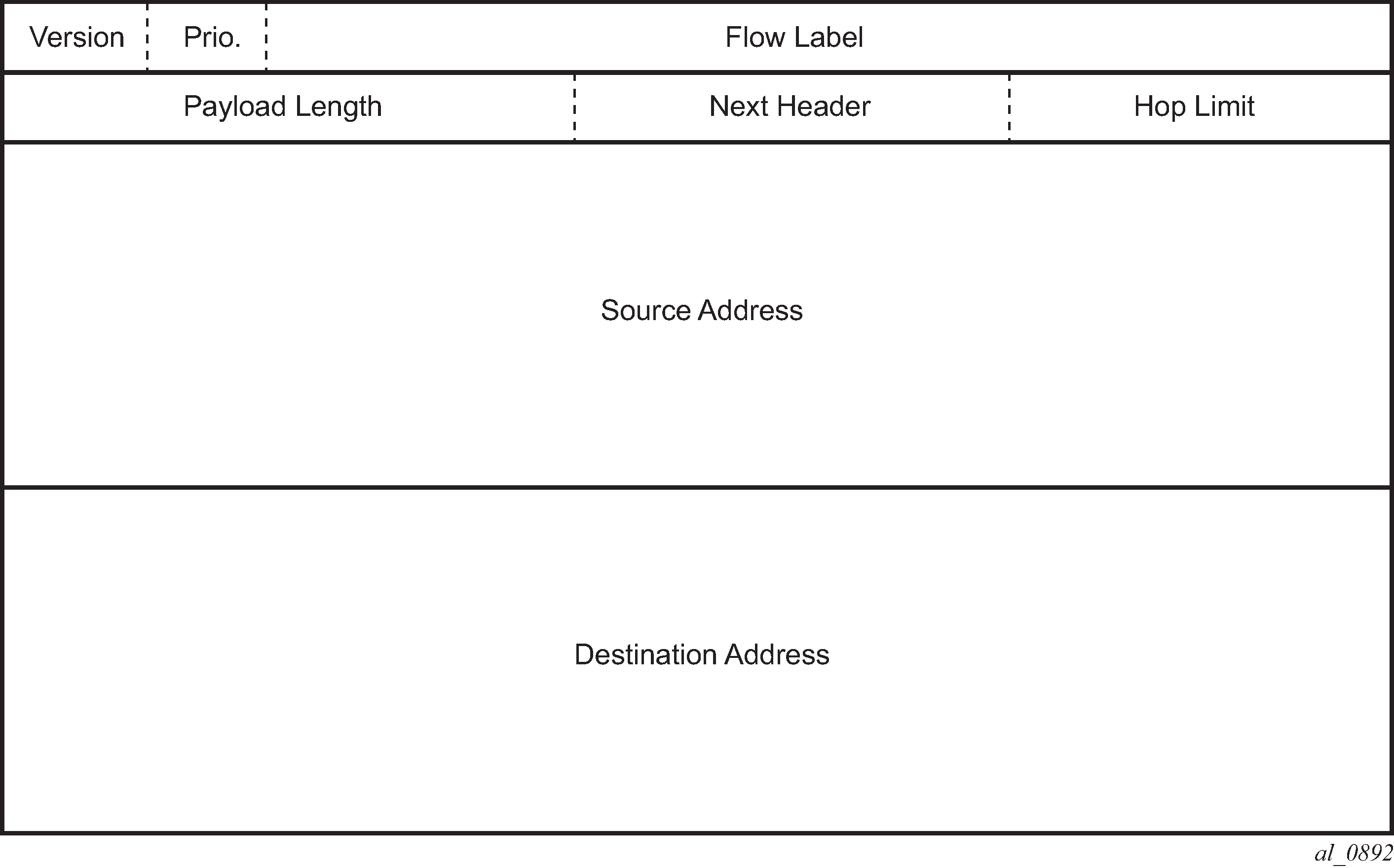
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Version |
4-bit Internet Protocol version number = 6 |
Prio. |
4-bit priority value |
Flow Label |
24-bit flow label. |
Payload Length |
16-bit unsigned integer; the length of payload, for example, the rest of the packet following the IPv6 header, in octets; if the value is zero, the payload length is carried in a jumbo payload hop-by-hop option |
Next Header |
8-bit selector; identifies the type of header immediately following the IPv6 header; this field uses the same values as the IPv4 protocol field |
Hop Limit |
8-bit unsigned integer; decremented by 1 by each node that forwards the packet; the packet is discarded if the hop limit is decremented to zero |
Source Address |
128-bit address of the originator of the packet. |
Destination Address |
128-bit address of the intended recipient of the packet (possibly not the ultimate recipient if a routing header is present) |