About this task
SR OS supports the node-protect extensions to the Remote LFA algorithm as described in RFC 8102.
Remote LFA follows a similar algorithm as TI-LFA but does not limit the scope of the calculation of the extended P-Space and of the Q-Space to the post-convergence paths.
Remote LFA adds an extra forward SPF on behalf of the PQ node to ensure that for each destination the selected PQ node does not use a path via the protected node.
Figure: Application of the remote LFA algorithm for node protection shows a slightly modified topology from that in TI-LFA feature interaction and limitations. A new node R7 is added to the top ring and the metric for link R3-R6 is modified to 100.
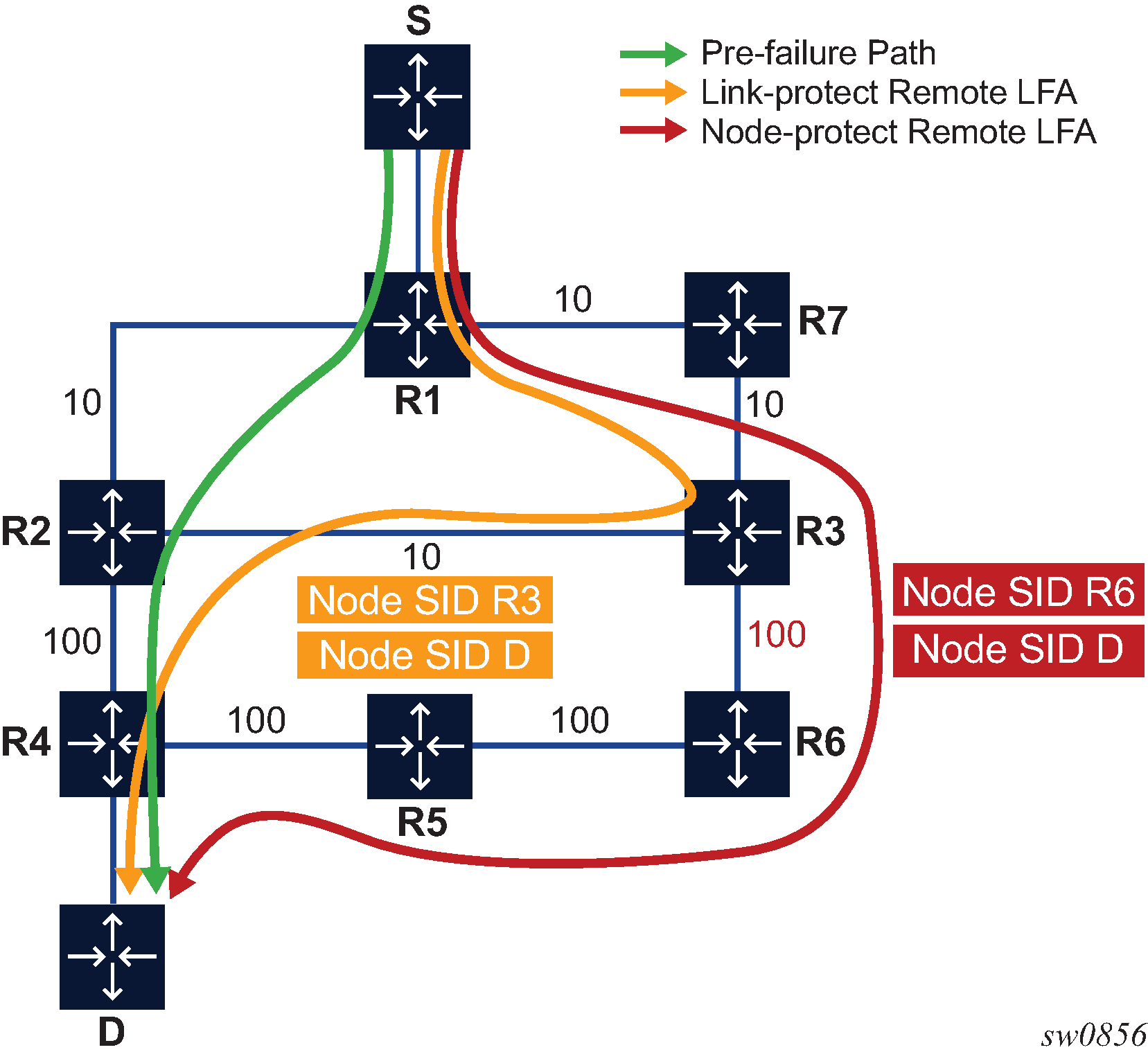
Applying the node protect remote LFA algorithm to this topology yields the following steps:
Procedure
What to do next
For each destination prefix D, R1 programs the remote LFA backup path:
-
For prefixes of R5, R4 or downstream of R4, R1 programs a node-protect remote LFA repair tunnel to the PQ node R6 by pushing the SID of node R6 on top of the SID for destination D and programming a next hop of R7.
-
For prefixes owned by node R2, R1 runs the link-protect remote LFA algorithm and programs a simple link-protect repair tunnel which consists of a backup next hop of R7 and pushing the SID of PQ node R3 on top of the SID for the destination prefix D.
-
Prefixes owned by nodes R7, R3, and R6 are not impacted by the failure of R2 because their primary next hop is R7.