The DS-Lite feature is supported on the 7710 SR-Series in combination with the MS-ISA to function as a DS-Lite Address Family Transition Router (AFTR).
DS-Lite is an IPv6 transition technique that allows tunneling of IPv4 traffic across an IPv6-only network. Dual-stack IPv6 transition strategies allow service providers to offer IPv4 and IPv6 services and save on OPEX by allowing the use of a single IPv6 access network instead of running concurrent IPv6 and IPv4 access networks. DS-Lite has two components: the client in the customer network, known as the Basic Bridging BroadBand element (B4) and an Address Family Transition Router (AFTR) deployed in the service provider network.
DS-Lite leverages a network address and port translation (NAPT) function in the service-provider AFTR element to translate traffic tunneled from the private addresses in the home network into public addresses maintained by the service provider. On the 7750 SR, this is facilitated through the Carrier Grade NAT function.
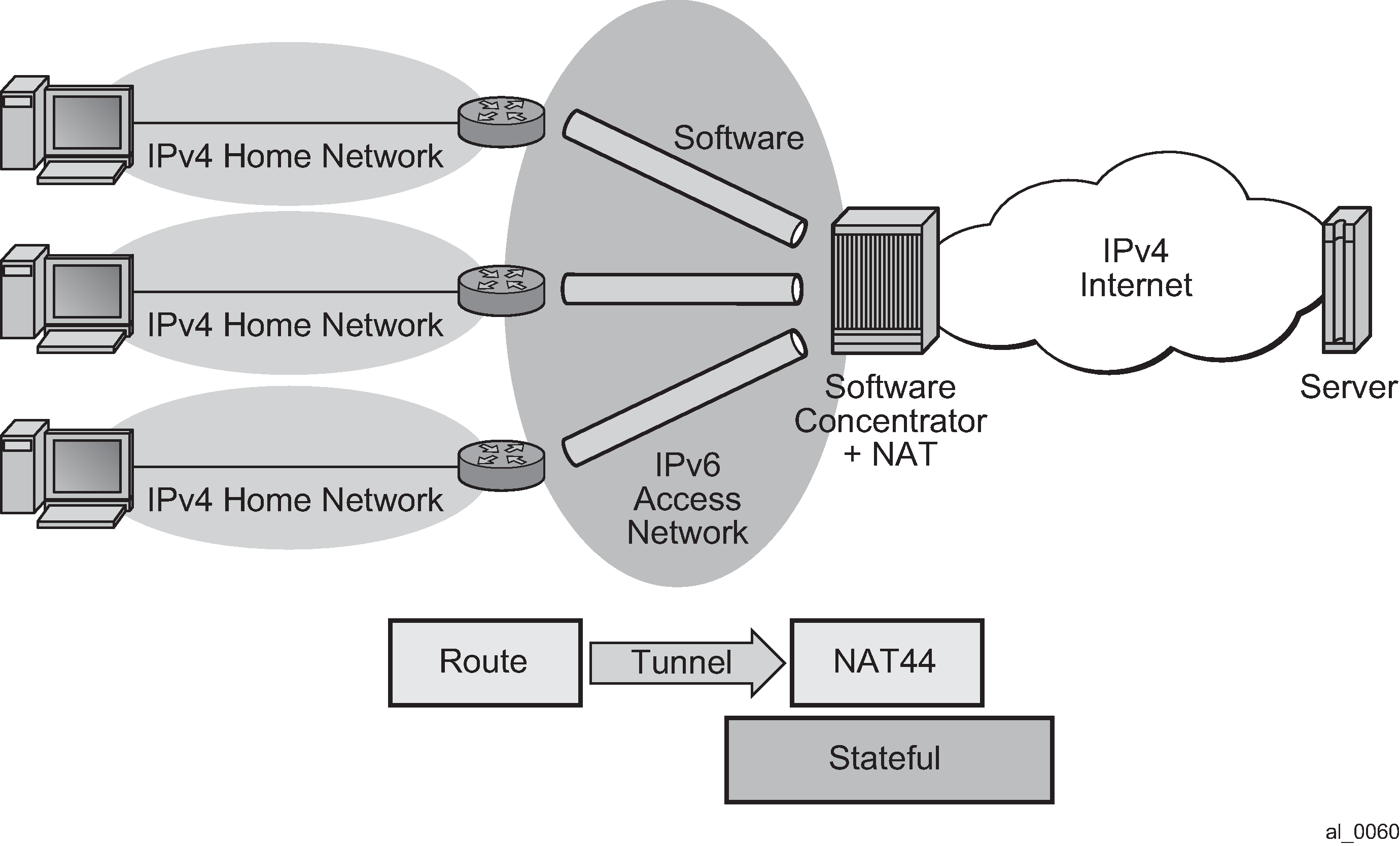
As shown in Figure: Dual-Stack Lite, DS-Lite has two components, a softwire initiator in the RG and a softwire concentrator, deployed in the service provider network, where control-less IP-in-IP (using protocol 4 - IPv4 in IPv6) is used for tunneling. When using control-less protocol, packets are sent on the wire for the remote softwire endpoint without prior setup of a tunnel.
The softwire initiator in the home network is combined with a routing function, where the default route is passed to the softwire pseudo-interface. Note that there is no NAT function, therefor, the private IP addresses of the home network are encapsulated without source address modification, and forwarded to the softwire concentrator where all NAT is performed. The softwire pseudo-interface unicasts all IPv4 traffic to the IPv6 address of the softwire concentrator, which was pre-configured.
When encapsulated traffic reaches the softwire concentrator, the device treats the source-IP of the tunnel to represent a unique subscriber. The softwire concentrator performs IPv4 network address and port translation on the embedded packet by re-using Large Scale NAT and L2-Aware NAT concepts.