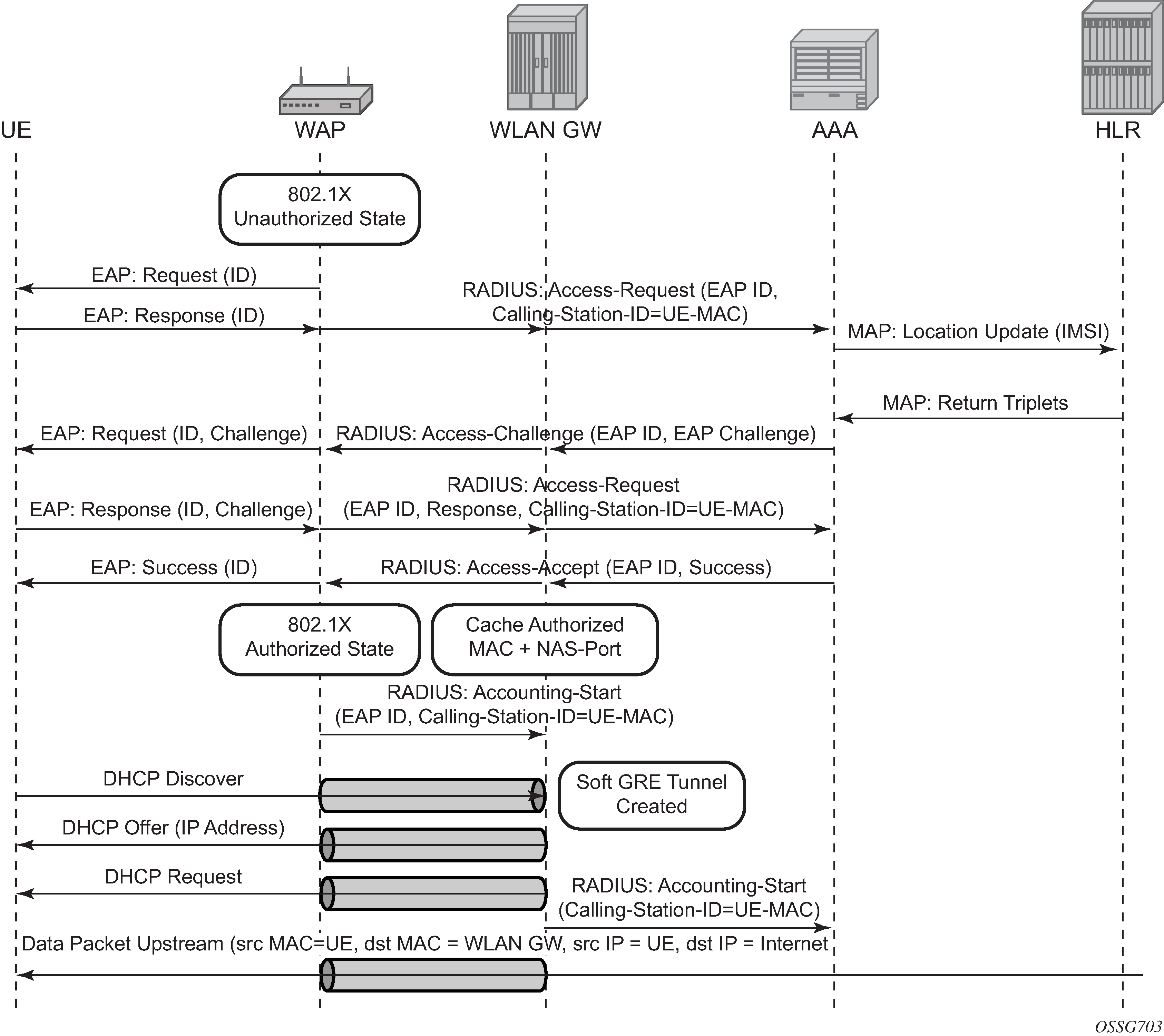
In this model the Wi-Fi AP supports a RADIUS client and originates RADIUS messages based on 802.1x/EAP exchange with the UE. It sends EAP payload in RADIUS messages toward the RADIUS server or RADIUS proxy. 7750 WLAN-GW can be configured as a RADIUS proxy for the Wi-Fi APs. The Wi-Fi AP should be configured with the IP address of the RADIUS proxy, and should send authentication and accounting messages non-tunneled, natively routed to the RADIUS proxy. See Figure: EAP authentication call flow with WLAN-GW RADIUS proxy.
The RADIUS proxy function allows 7750 SR to look at the RADIUS authentication and accounting messages and create or update corresponding subscriber state. RADIUS proxy transparently forwards RADIUS messages between AP (authenticator) and the AAA server. The access-request message contains standard RADIUS attributes (including username), and the EAP payload. Standard authentication algorithms negotiated with EAP involve multiple round-trips (challenge/response) between AP (and UE) and the AAA server.
After authentication is complete, AAA server passes back subscriber related configuration parameters as well as the computed session keys (Pairwise Master Key (PMK)) for 802.11i to the AP. These keys are encrypted using shared secret between AP (authenticator) and the AAA server. 7750 SR WLAN-GW can optionally cache authentication information of the subscriber from access-request and access-accept messages. The cached information allows local authorization of subsequent DHCP messages from the UEs behind the AP against the cached state on the 7750 SR RADIUS proxy and avoids another trip to the RADIUS server.