This solution set adds support for managing subscribers gaining network access over WLAN. The WLAN access enables a service provider to offer a mobile broadband service to its subscribers or to offload traffic on its or a partner’s macro cellular (3G/4G) network. The WLAN access can be from public hot-spots (indoor or outdoor APs), venues, enterprises, or home-spots (with public SSID).
The 7750 SR serves as a WLAN Gateway (WLAN-GW) providing Layer 3 termination and ESM for these subscribers. The connectivity from WLAN AP or AC can be over any existing access technology (DSL, PON, Fiber, DOCSIS, and so on), with Ethernet based connectivity from the access node (DSLAM, OLT, Eth MTU, Layer 2 CMTS) to the WLAN-GW. WLAN-GW functions could be on a standalone 7750 as shown in Figure: Standalone WLAN-GW or could be an add-on functionality on existing 7750 based BNG as shown in Figure: WLAN-GW functions on existing BNG. WLAN connectivity to the WLAN-GW could be over a Layer 2 aggregation or an Layer 3 aggregation network (typical when WLAN-GW is upstream of an existing BNG or CMTS). In case of Layer 2 aggregation the connectivity to the WLAN-GW could be tagged or untagged Ethernet. In case of Layer 3 aggregation, supported connectivity option is Ethernet over GRE (or Eth-over-MPLS over GRE) tunnel originating from the AP/AC, and terminating on the WLAN-GW. The WLAN AP acts as a bridge, switching Ethernet frames into a GRE tunnel terminating on an MS-ISA in the WLAN-GW.
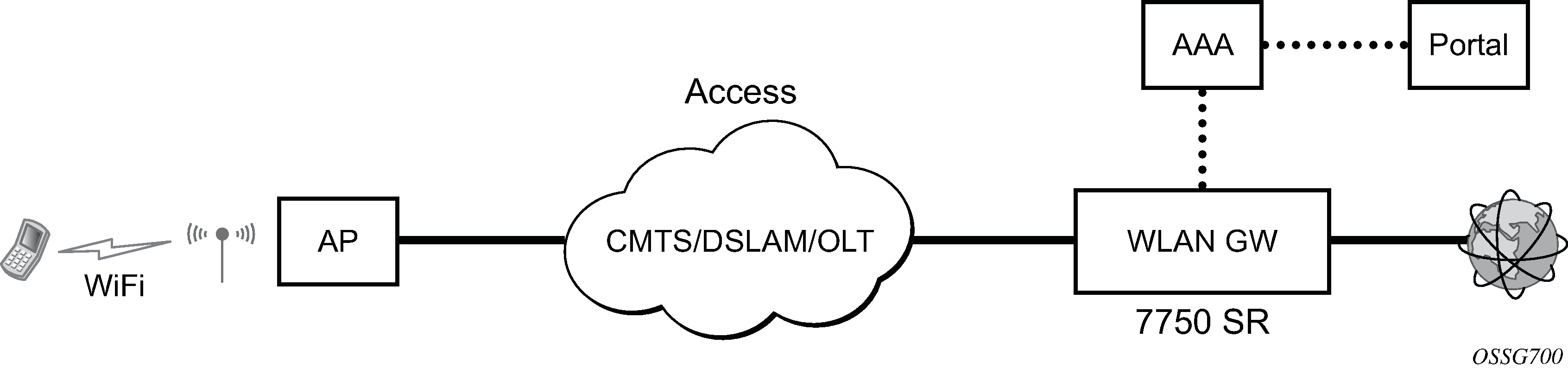
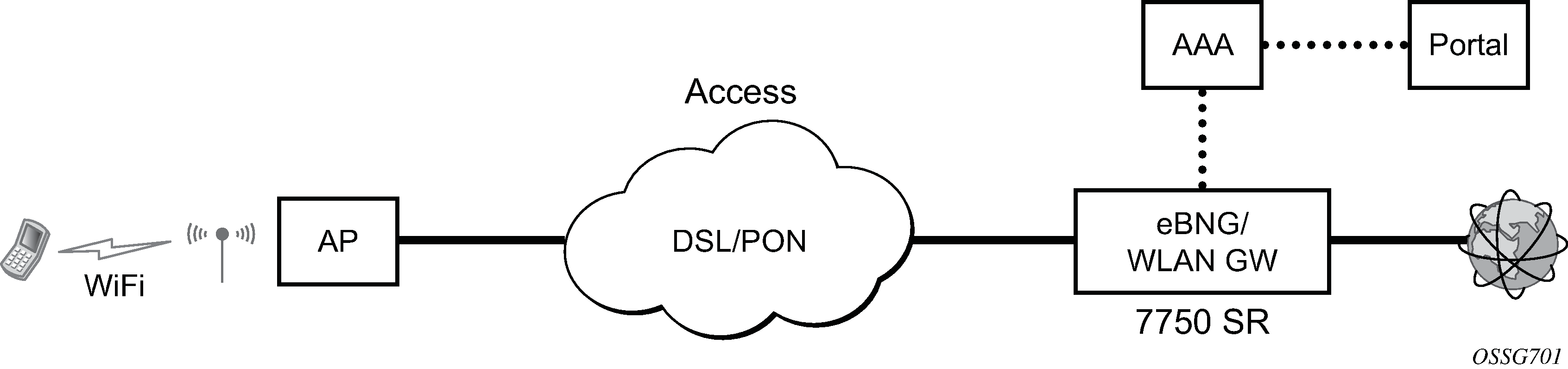
AP Connectivity to the WLAN-GW could be direct Ethernet (tagged or untagged) or could be Ethernet over GRE. With the bridged AP using GRE tunnels, the WLAN-GW solution elements are discussed in the following sections.