The 7705 SAR supports the ITU-T Y.1564 feature for throughput and bandwidth testing of Ethernet point-to-point virtual circuits. ITU-T Y.1564 includes, but also improves and standardizes, the RFC 2544 testing process.
ITU-T Y.1564 is supported on second-generation Ethernet ports in access mode in conjunction with 16-priority scheduling, on the following:
7705 SAR-A
7705 SAR-Ax
7705 SAR-H (not supported on the 4-port SAR-H Fast Ethernet module)
7705 SAR-Hc
7705 SAR-M
7705 SAR-Wx
8-port Gigabit Ethernet Adapter card
10-port 1GigE X-Adapter card (in 10-port 1GigE mode)
Packet Microwave Adapter card
ITU-T Y.1564 is supported on third-generation Ethernet ports in access mode in conjunction with 4-priority scheduling, on the following:
7705 SAR-X
6-port Ethernet 10Gbps Adapter card
For information about card and platform generations, see the 7705 SAR Interface Configuration Guide, "Evolution of Ethernet Adapter Cards, Modules, and Platforms".
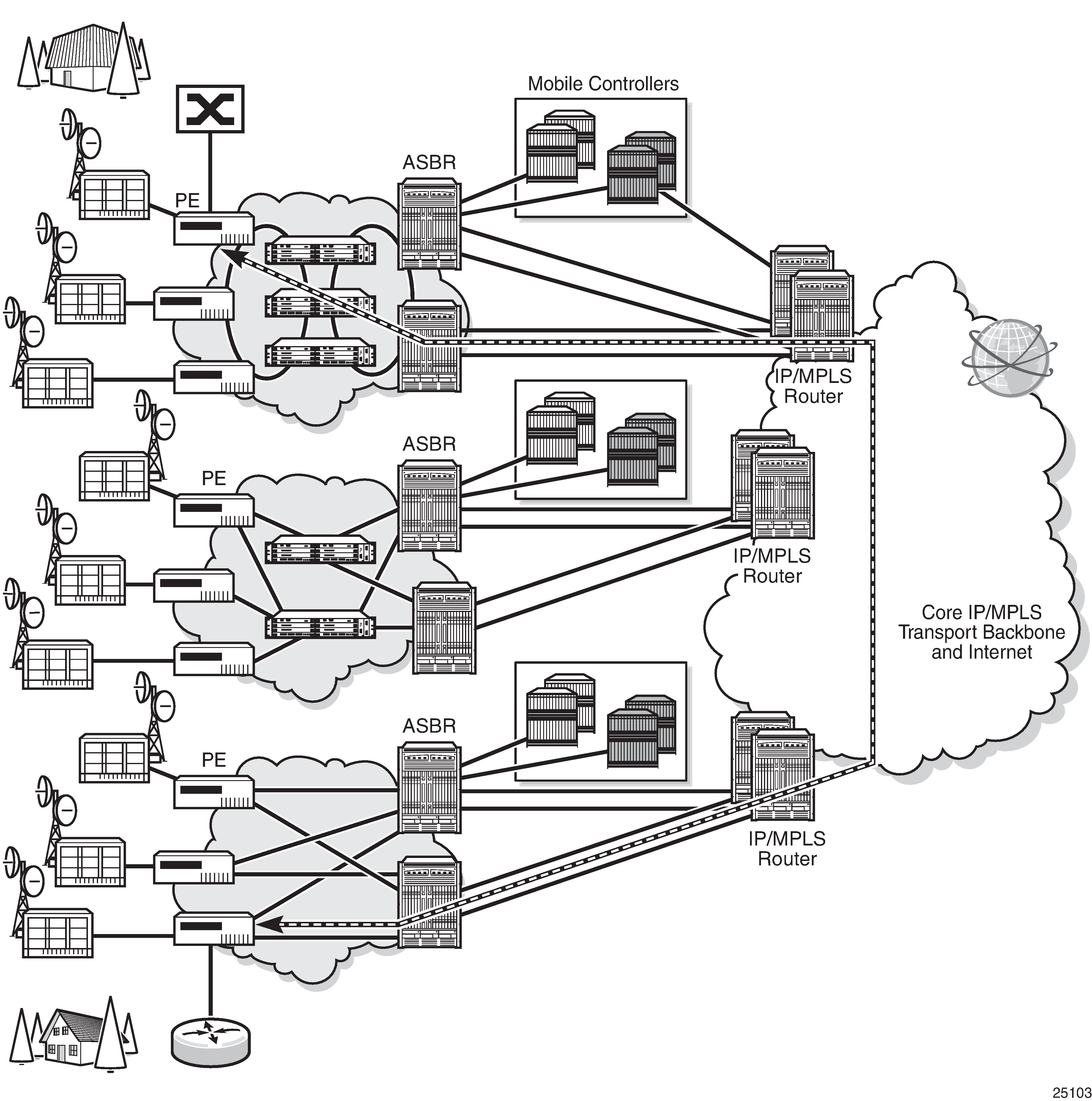
In a traditional hub and spoke network model, traffic is terminated on edge routers and aggregation hubs, which also perform bandwidth and throughput tests. In a flat, seamless, MPLS network, edge routers and aggregation hubs provide only forwarding and switching and cannot be used for service testing as they do not terminate traffic.
ITU-T Y.1564 is crucial in these types of networks because it provides the 7705 SAR edge nodes with the ability to run a complete validation of Ethernet SLAs. The 7705 SAR generates RFC 2544 test frames, up to the required rate, and sends them through the SAP of the service to test its performance. The far-end nodes must also offer per-service loopback capabilities, with the epipe>sap>loopback command, to return the traffic to the source node for test analysis and reporting.
Figure: ITU-T Y.1564 End-to-End Throughput Test shows a network with service endpoints where throughput tests are required.
During an ITU-T Y.1564 test, marker frames are used to measure delay and jitter. Packet loss is reported directly by counting transmitted and received frames. Delay, jitter, and loss support two profile states: conforming traffic (configured as in-profile) and non-conforming traffic (configured as out-of-profile).
The 7705 SAR relies on the SAP ingress and SAP egress QoS profile queuing points for generated test traffic bandwidth. The assigned CIR and PIR dictate the potential test frame coloring when a Y.1564 test is run with color-aware enabled.
The following colors are assigned to packets:
green — traffic is equivalent to the CIR
yellow — traffic received, up to the SAP PIR provisioned value
red — traffic exceeding the PIR provisioned value
Figure: Queuing and Policing Points That Impact Throughput shows all of the queuing and policing points, in addition to the SAP ingress QoS profile, that can have an effect on the throughput test results. Each of these queuing points can contribute to traffic policing or shaping, which can impact delay, jitter, and loss measurements.
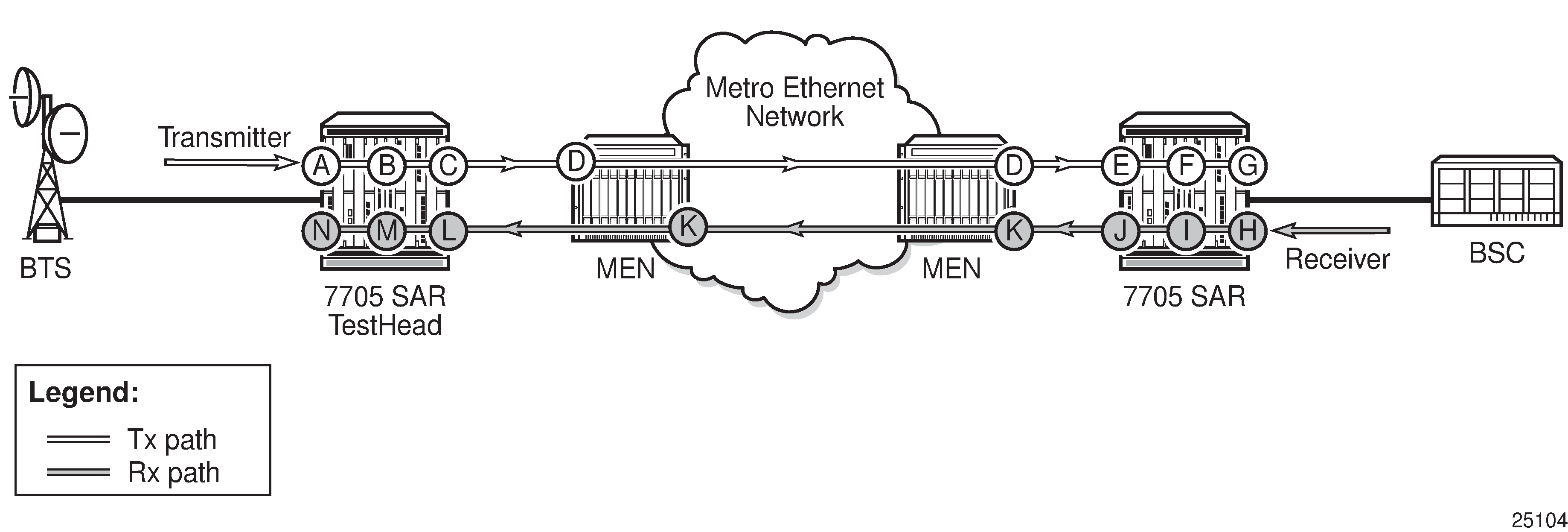
| Point | Description | Point | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
A |
Test head access/SAP ingress QoS profile |
H |
Far-end/responder access/SAP ingress QoS profile |
|
B |
Test head access ingress fabric shaper |
I |
Far-end/responder access ingress fabric shaper |
|
C |
Test head network egress QoS profile |
J |
Far-end/responder network egress QoS profile |
|
D |
Any QoS enforcement via intermediate LSR nodes |
K |
Any QoS enforcement via intermediate LSR nodes |
|
E |
Far-end/responder network ingress QoS profile |
L |
Test head network ingress QoS profile |
|
F |
Far-end/responder network ingress fabric shaper |
M |
Test head network ingress fabric shaper |
|
G |
Far-end/responder access/SAP egress QOS profile |
N |
Test head access/SAP egress QoS profile |