In general, EVPN multihoming is supported in Inter-AS Option B or VPN-NH-RR networks with the following limitations:
An ES PE can only process a remote ES route correctly if the received next hop and origination IP address match. EVPN multihoming is not supported when the ES PEs are in different ASs or IGP domains, or if there is an NH-RR peering the ES PEs and overriding the ES route next hops.
EVPN multihoming ESs are not supported on EVPN PEs that are also ABRs or ASBRs.
Mass-withdraw based on the AD per-ES routes is not supported for a PE that is in a different AS or IGP domain that the ES PEs. Figure: EVPN multihoming with inter-AS Option B or VPN-NH-RR shows an EVPN multihoming scenario where the ES PEs, PE2 and PE3, and the remote PE, PE1, are in different ASs or IGP domains.
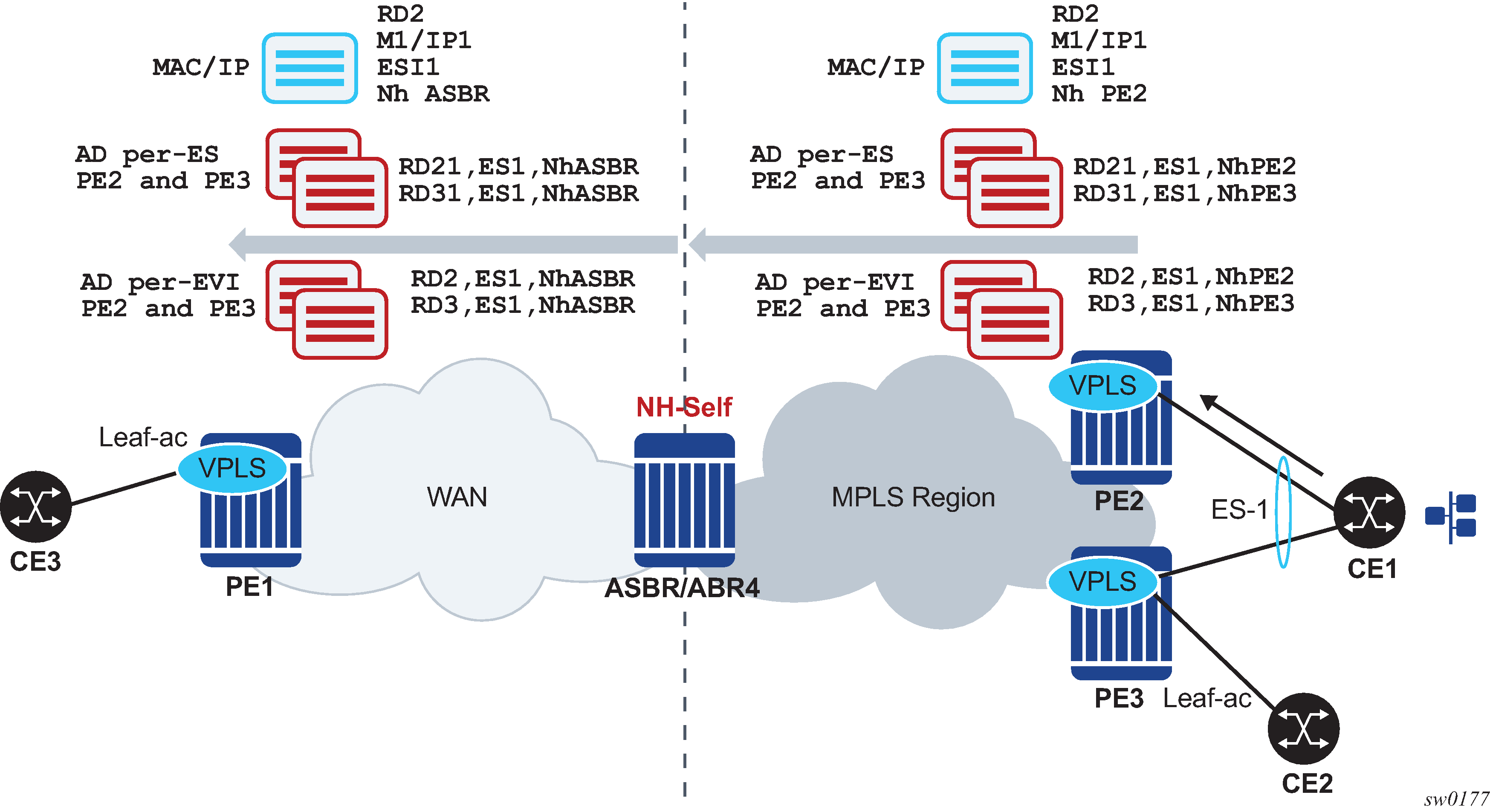
In Figure: EVPN multihoming with inter-AS Option B or VPN-NH-RR, PE1’s aliasing and backup functions to the remote ES-1 are supported. However, PE1 cannot identify the originating PE for the received AD per-ES routes because they are both arriving with the same next hop (ASBR/ABR4) and RDs may not help to correlate each AD per-ES route to a specified PE. Therefore, if there is a failure on PE2’s ES link, PE1 cannot remove PE2 from the destinations list for ES-1 based on the AD per-ES route. PE1 must wait for the AD per-EVI route withdrawals to remove PE2 from the list. In summary, when the ES PEs and the remote PE are in different ASs or IGP domains, per-service withdrawal based on AD per-EVI routes is supported, but mass-withdrawal based on AD per-ES routes is not supported.