Inter-AS Option B and Next-Hop-Self Route-Reflector (VPN-NH-RR) functions are supported for the BGP-EVPN family in the same way both functions are supported for IP-VPN families.
A typical use case for EVPN Inter-AS Option B or EVPN VPN-NH-RR is Data Center Interconnect (DCI) networks, where cloud and service providers are looking for efficient ways to extend their Layer 2 and Layer 3 tenant services beyond the data center and provide a tighter DC-WAN integration. While the instantiation of EVPN services in the DGW to provide this DCI connectivity is a common model, some operators use Inter-AS Option B or VPN-NH-RR connectivity to allow the DGW to function as an ASBR or ABR respectively, and the services are only instantiated on the edge devices.
Figure: EVPN inter-AS Option B or VPN-NH-RR model shows a DCI example where the EVPN services in two DCs are interconnected without the need for instantiating services on the DC GWs.
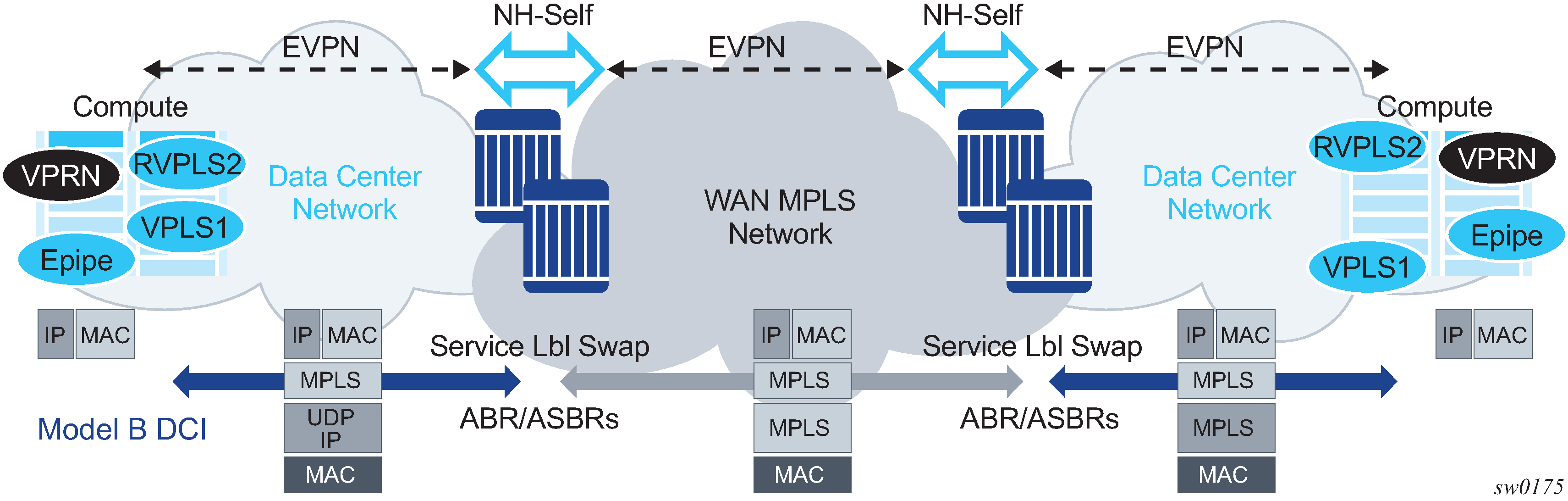
The ASBRs or ABRs connect the DC to the WAN at the control plane and data plane levels where the following considerations apply:
From a control plane perspective, the ASBRs or ABRs perform the following tasks:
-
accept EVPN-MPLS routes from a BGP peer
EVPN-VXLAN routes are not supported.
-
extract the MPLS label from the EVPN NLRI or attribute and program a label swap operation on the IOM
-
re-advertise the EVPN-MPLS route to the BGP peer in the other Autonomous Systems (ASs) or IGP domains
The re-advertised route has a Next-Hop-Self and a new label encoded for those routes that came with a label.
-
From a data plan perspective, the ASBRs and ABRs terminate the ingress transport tunnel, perform an EVPN label swap operation, and send the packets on to an interface (if E-BGP is used) or a new tunnel (if IBGP is used).
The ASBR or ABR resolves the EVPN routes based on the existing bgp next-hop-resolution command for family vpn, where vpn refers to EVPN, VPN-IPv4, and VPN-IPv6 families.
*A:ABR-1# configure router bgp next-hop-resolution labeled-routes transport-tunnel
family vpn resolution-filter
- resolution-filter
[no] bgp - Use BGP tunnelling for next hop resolution
[no] ldp - Use LDP tunnelling for next hop resolution
[no] rsvp - Use RSVP tunnelling for next hop resolution
[no] sr-isis - Use sr-isis tunnelling for next hop resolution
[no] sr-ospf - Use sr-ospf for next hop resolution
[no] sr-te - Use sr-te for next hop resolution
[no] udp - Use udp for next hop resolution
For more information about the next-hop resolution of BGP-labeled routes, see the 7450 ESS, 7750 SR, 7950 XRS, and VSR Unicast Routing Protocols Guide
Inter-AS Option B for EVPN services on ABSRs and VPN-NH-RR on ABRs re-use the existing commands enable-inter-as-vpn and enable-rr-vpn-forwarding respectively. The two commands enable the ASBR or ABR function for both EVPN and IP-VPN routes. These two features can be used with the following EVPN services:
EVPN-MPLS Epipe services (EVPN-VPWS)
EVPN-MPLS VPLS services
EVPN-MPLS R-VPLS services
PBB-EVPN and PBB-EVPN E-Tree services
EVPN-MPLS E-Tree services
PE and ABR functions (EVPN services and enable-rr-vpn-forwarding), which are both supported on the same router
PE and ASBR functions (EVPN services and enable-inter-as-vpn), which are both supported on the same router
The following sub-sections clarify some aspects of EVPN when used in an Inter-AS Option B or VPN-NH-RR network.