BFRs establish BIER adjacencies through IS-IS and exchange their BFR prefixes and BIER IDs as well as transport-related information. IS-IS can be used to exchange the information. Figure: BIER IGP sub-TLV shows the IS-IS extensions for BIER and Figure: BIER MPLS sub-sub-TLV shows a BIER MPLS sub-sub-TLV.
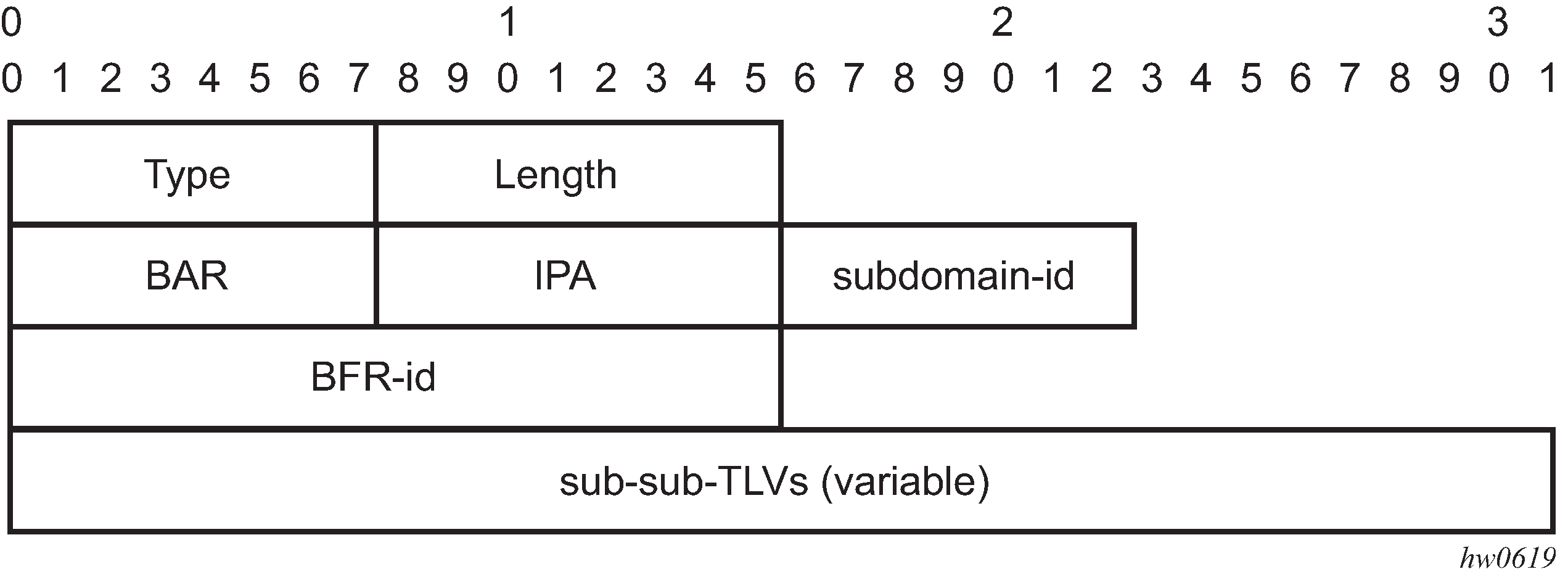
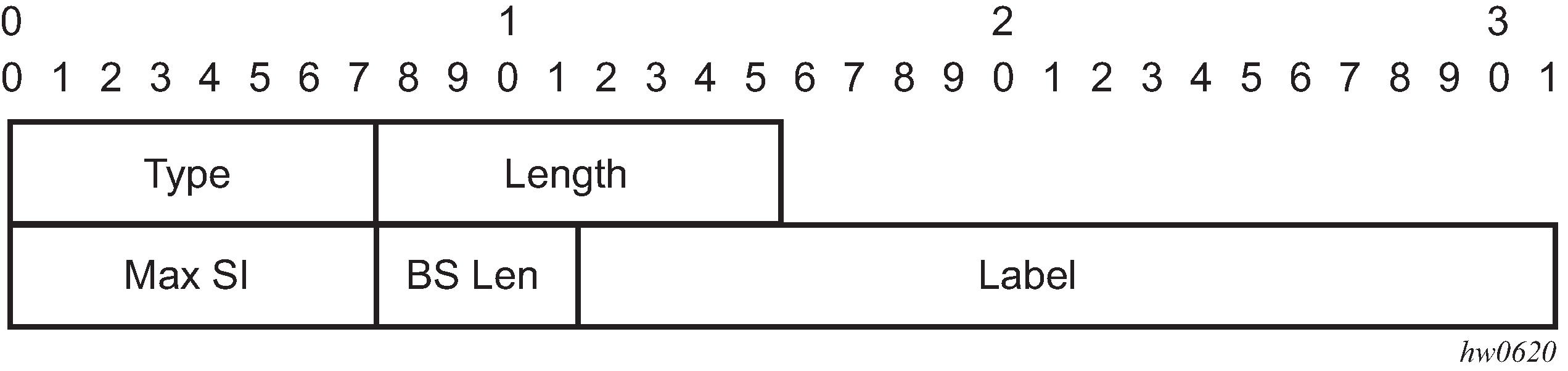
In IS-IS, a new BIER sub-TLV is advertised as part of extended prefix opaque LSA carrying the BFR IP address (loopback) and supported BIER bitmask length for this BFR (multiple TLVs are used to convey support for multiple bitmask lengths). In addition, when MPLS encapsulation is used, a BIER MPLS encapsulation sub-TLV is included that contains the label range used for BIER. The label ranges advertised within the area are unique to a BFR and are used to identify the BIER forwarding context.
Based on the information exchanged, IGP creates a BIER routing table (unicast SPF) to reach each BFER that can be used to route BIER packets. The routing table specifies the shortest unicast path to reach each BFER through (BFERs bitmask, next-hop BFR)-tuples.
BIER sub-TLVs having the wrong length or illegal encoding are ignored and no error is raised. All other sub-TLV or sub-sub-TLV validation is done by the BIER module.