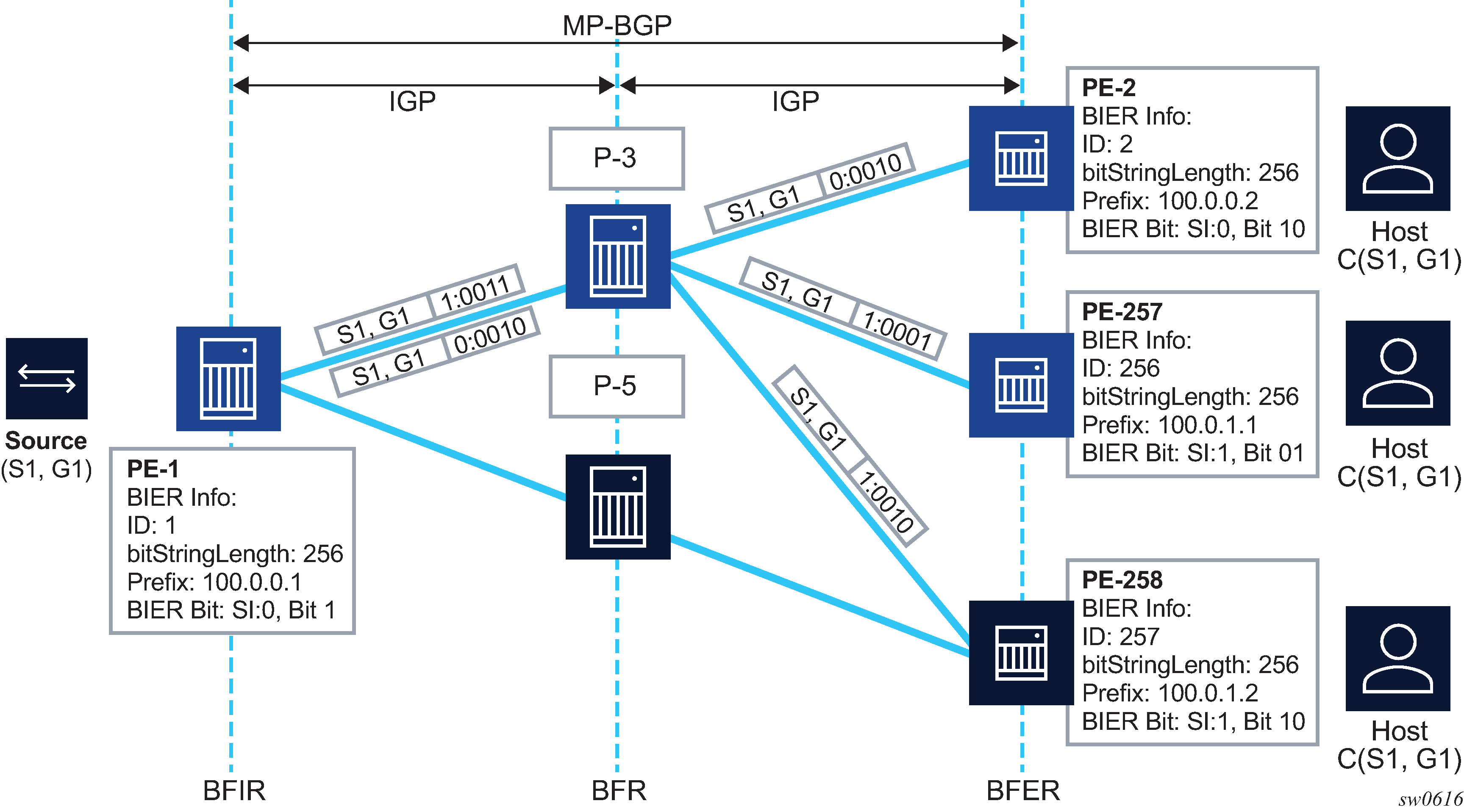
Figure: BIER high-level IGP and overlay shows multicast with BIER deployed. IGP is used as the routing underlay, and MP-BGP for NG-MVPN is used as the multicast flow overlay. The BFIR is the source PE-1, BFERs 2, 256, and 257 are receiver PEs, and the remaining routers are BFRs. All routers have their BIER prefix assigned and, additionally, the BFERs have BIER BFR-IDs assigned.
A BFR prefix is a unicast routable IP address (either IPv4 or IPv6) that is either a system loopback or a loopback interface. BFR prefixes are unique within a BIER domain.
A BFR ID is a unique number assigned to BFERs and BFIRs that is used to build the BIER bitmask used to forward packets. BIER IDs should be allocated as a continuous set of IDs starting at 1 to ensure a minimum number of sets are required to achieve multicast BIER connectivity. Sets allow scaling of BIER beyond the bitmask length supported; however, sets require a separate copy of the multicast packet to be forwarded on the same link which may result in unwanted replication.