To increase scalability of BIT String Length (BSL), routers can be grouped into BIER sets.
The BSL dictates how many BFRs can be represented in a BIER set. Each BIER set can contain as many routers as the length of BSL, and it is represented by a BIER Set ID (SI). The Set ID is part of the packet and represented as <SI:Bit Position>. Figure: BIER set shows an example set with a BSL of 4.
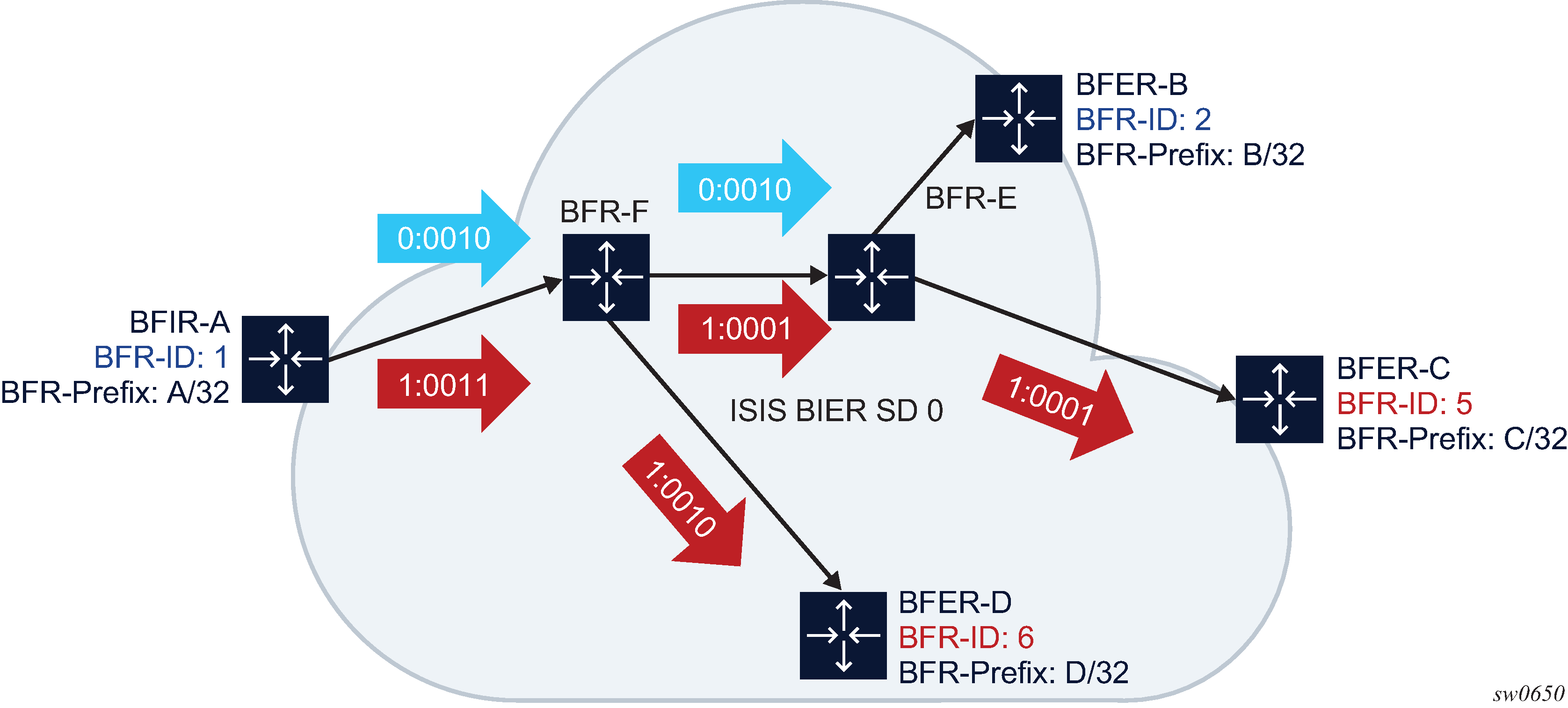
The BFR ID is programmed into <SI, Bit Position> based on the network BSL.
SI = (BFR-ID – 1)/BSL
BP = ((BFR-ID – 1) mod BSL)+1
For example: BSL 4 and BFR-ID 6 = <SI=1, BP=2>.
BIER works well in an IP TV deployment where the network is in a spine and leaf deployment. SR OS supports 16 set IDs in this type of deployment where there is no packet duplication at the spine.
The SHO can be connected to as many as 16 VHOs.
Each tree can have 256 LEAFs without packet duplication.
Each leaf can have as many hosts on it as the number of supported IGMP/MLD hosts.