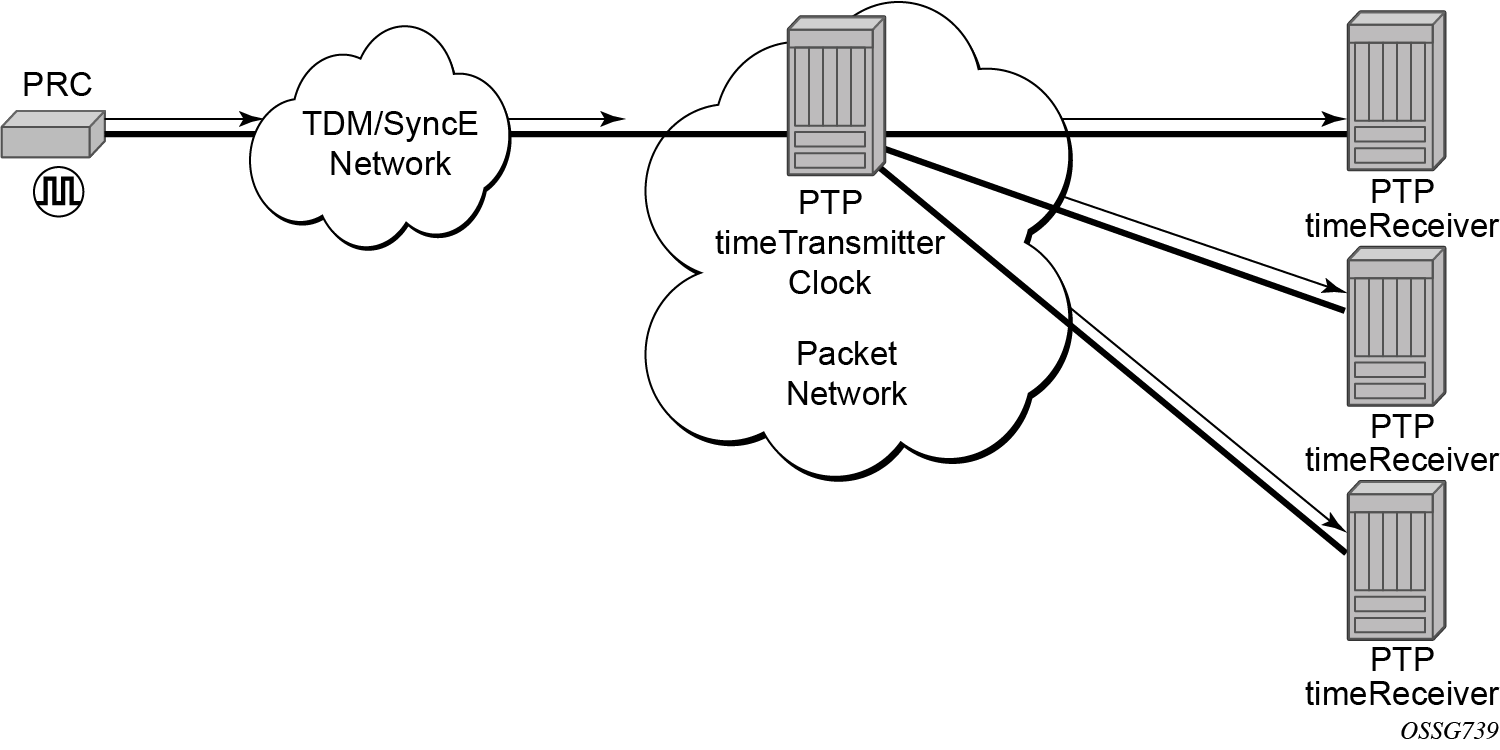
The router supports the PTP ordinary clock in timeTransmitter mode. Normally, an IEEE 1588v2 grandmaster is used to support many timeReceivers and boundary clocks in the network. In cases where only a small number of timeReceivers and boundary clocks exist and only frequency is required, a PTP integrated timeTransmitter clock can greatly reduce hardware and management costs to implement PTP across the network. It also provides an opportunity to achieve better performance by placing a timeTransmitter clock closer to the edge of the network, as close to the timeReceiver clocks as possible. Figure: PTP timeTransmitter clock shows a PTP timeTransmitter clock network configuration.
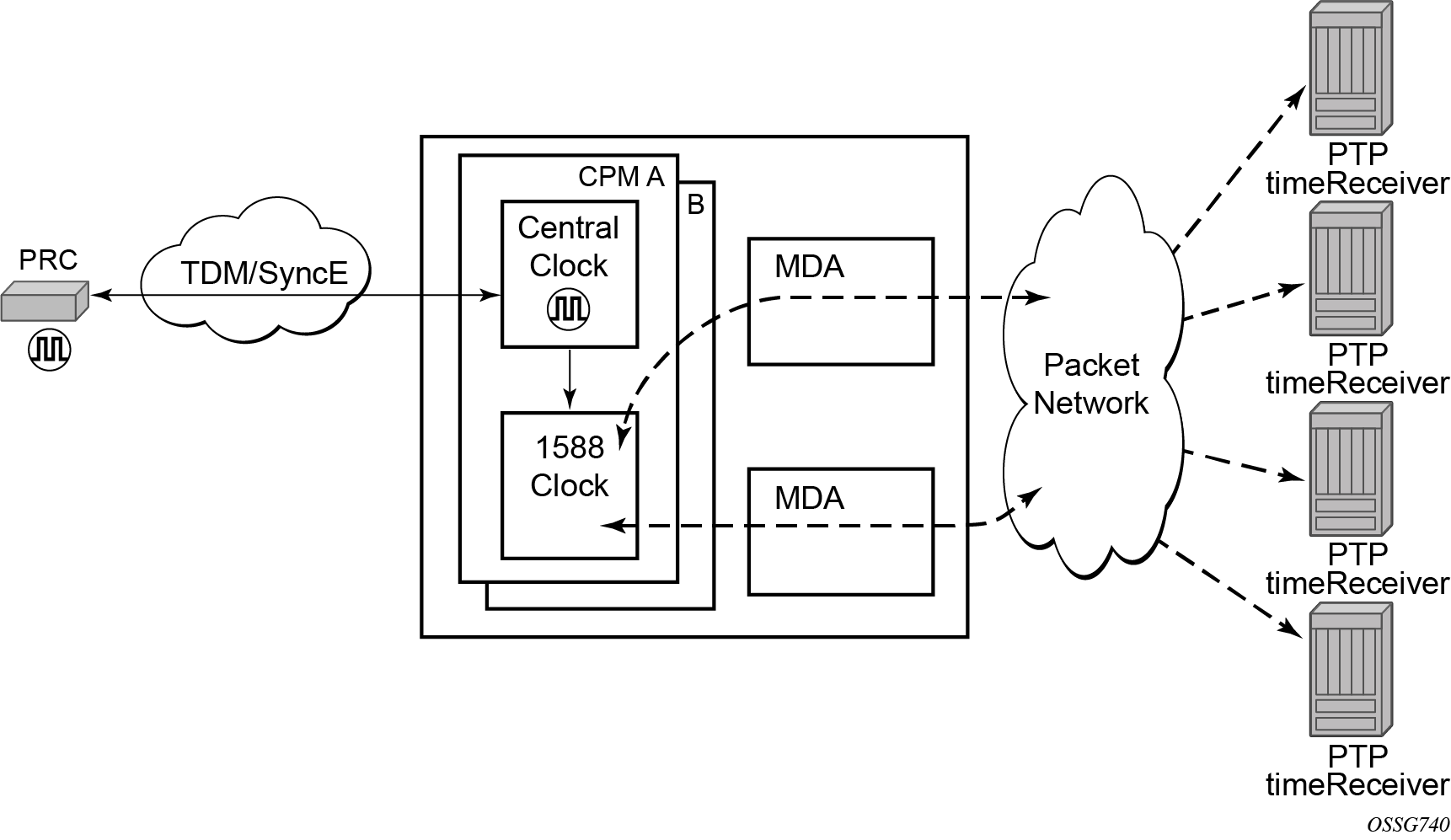
All packets are routed to their destination via the best route as determined in the route table; see Figure: Ordinary timeTransmitter clock operation. It does not matter which ports are used to ingress and egress these packets (unless port based time stamping is enabled for higher performance).