IP fragmentation is only supported for L2oGRE with IPv4 transport. Traffic is subjected to several MTU checks in the downstream direction (toward the remote end of the L2oGRE tunnel) within the SR OS node, as shown in Figure: L2oGRE MTUs.
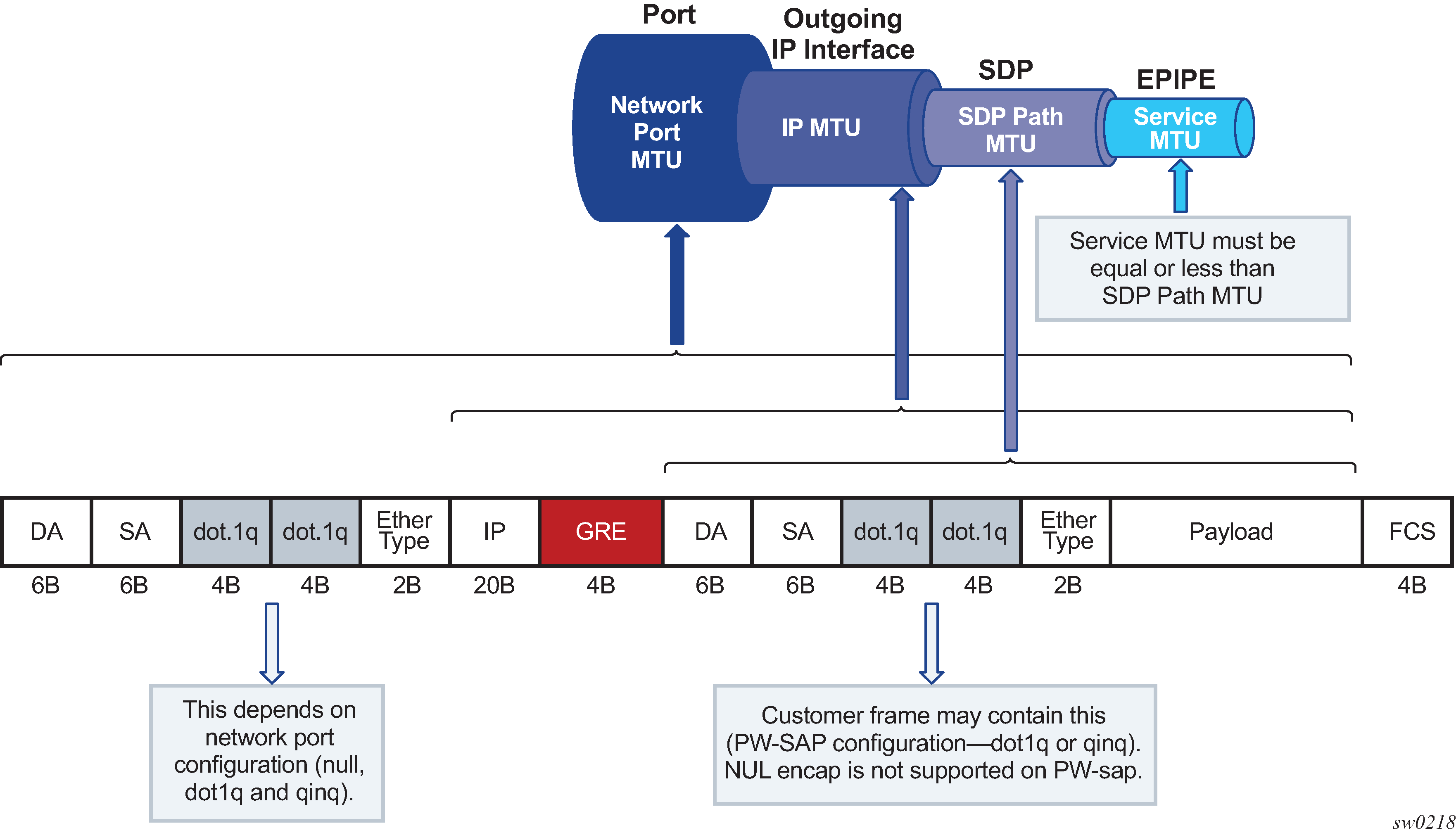
In the example:
Port MTU represents the maximum frame size on the outgoing physical port.
IP MTU is the maximum IP packet size on the outgoing IP interface.
SDP Path MTU represents the maximum size of a frame that is encapsulated with the GRE tunnel. Its value is determined by the smallest MTU size on the path between the two GRE tunnel terminating end-points. The SDP Path MTU is calculated automatically by subtracting transport IP and GRE header bytes from the configured IP MTU of the outgoing interface.
Service MTU indicates the maximum frame size that the customer can accept over the service (PW SAP). Its value is determined by the MTU size within the customer's network. The service MTU is configured within the VC-switching Epipe that stitches the L2oGRE spoke SDP to a PW port. The default value is set to 1514 bytes.
MTU values:
Figure: ESM termination shows an example of IPv4 as the GRE delivery protocol.
Port MTU = 1600 bytes (this is operator's configured value)
IP MTU (of the outgoing interface) = 1600 bytes- 22 bytes= 1578 bytes (this is operator's configured value)
SDP Path MTU = automatically calculated and set to 1578 bytes - 24 bytes = 1554 bytes.
Service MTU = This value must be configured to a value no higher than 1554 bytes (SDP Path MTU).
Frames within an SR OS cannot be fragmented on a service or SDP level. However, L2oGRE traffic can be fragmented at the port level and for IPv4 traffic at any downstream point, if the DF bit in the IP header is cleared. The DF bit setting is controlled by the config>service>sdp>allow-fragmentation and config>service>pw-template>allow-fragmentation commands.
L2oGRE-v6 frames are subjected to the same MTU checks as IPv4 frames. However, IPv6 frames are not fragmented if their size exceeds MTU, and instead, are dropped.