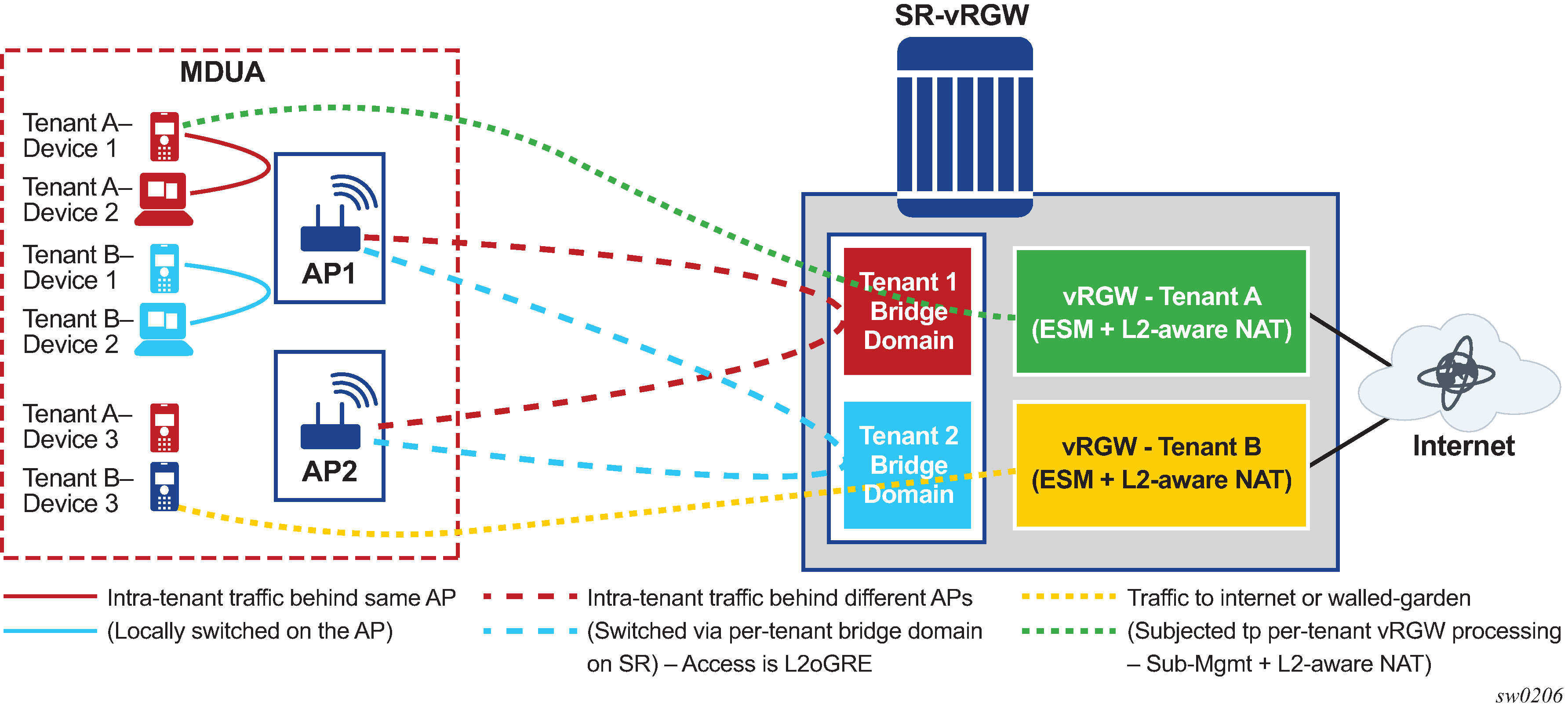
In a typical vRGW deployment, including HLE, the subscriber’s BRG instance and BD on vRGW are tied to an access circuit (such as a soft GRE or soft L2TPv3 tunnel) from a single bridged Access Point (AP) or a residential gateway (RG). This feature adds support for subscriber to be AP agnostic. This means that a subscriber’s BRG instance and BD are not tied to a single bridged AP or RG. This is particularly useful when the customer premise is an multi-dwelling (MDU) unit inhabited by multiple independent tenants where these tenants within the building can obtain connectivity from any bridged AP in the building. Bridged WIFI AP and RGs can be installed in various parts of the building and are not owned or operated by specific tenants. Each AP can be provisioned with a common SSID (for example, an operator-branded SSID providing bulk Internet access and intra-MDU connectivity). Each AP accesses the network by an L2oGRE or L2TPv3 tunnel terminating on a gateway (vRGW) that provides integrated bridging and vRGW processing. The existing vRGW functionality is defined in Virtual Residential Gateway. The per tenant (access) bridging function on vRGW is described in Home LAN Extension. With this AP agnostic access feature, the traffic flow is handled as follows (Figure: AP agnostic access – integrated bridging and vRGW processing).
Traffic between two devices of a tenant behind the same AP is locally switched by the AP.
Traffic between two devices belonging to the same tenant connecting from two different APs is not locally switched by the APs but is tunneled to the vRGW or gateway that provides a bridged domain per tenant. This traffic is bridged by the gateway using the per-tenant bridge-domain (BD).
Traffic between two devices belonging to different tenants connecting from the same or different AP in the building are tunneled to the gateway or vRGW. This traffic is subject to vRGW processing, such as ESM followed by L2-aware NAT. The isolation between tenants is provided by separate BRG contexts per tenant on the vRGW.
Traffic from a tenant device, connecting from any AP in the building, that is destined for any destination on the Internet is forwarded by the AP over the tunnel and is subject to vRGW processing; for example, ESM followed by NAT.