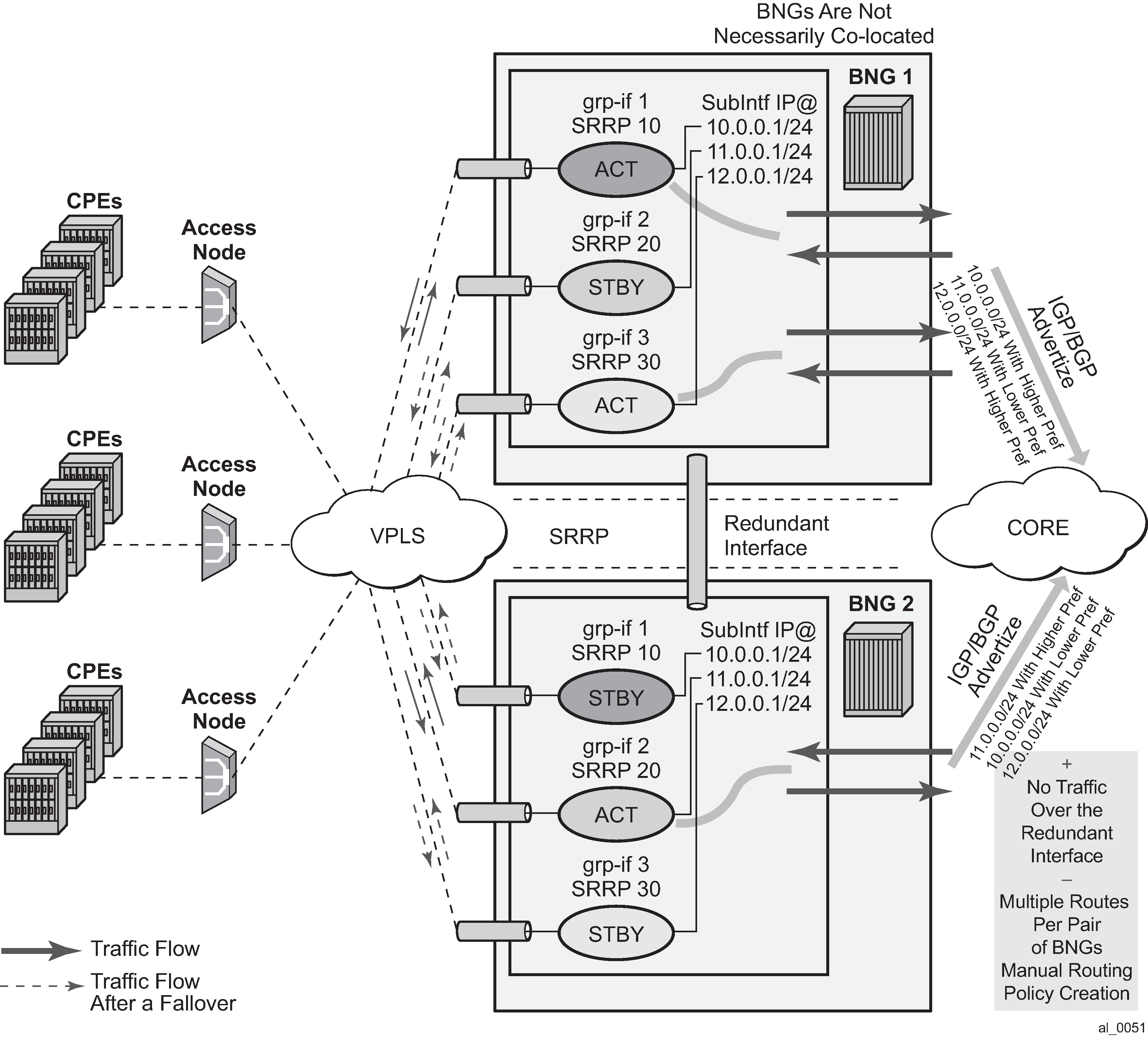
The SRRP enhancements addressed in this section is to reduce the need for redundant-interface between the pair of redundant nodes without sacrificing the subnet aggregation on the back-end.
Redundant BNG nodes are not always colocated. This means that the logical link associated with the redundant (shunt) interfaces is taking the uplink path therefore wasting valuable bandwidth (downstream traffic that arrives to the standby (SRRP backup state) node is routed by uplinks for the second time over to the active (SRRP master state) node).
To meet the requirement to reduce the existence of shunted traffic only to the short transitioning period between SRRP switchovers while the routing on the network side is converging, the following was required (referring to Figure: IP subnet per SRRP master group):
Share IP subnets over multiple SRRP instances. This is not mandatory, but it would help to load balance traffic over the two nodes. For example, IP subnets 10 and 11 can be shared over SRRP instances 10 and 20 on node 1, and the IP subnet 12 can be associated with the SRRP instance 30 on node 2.
SRRP aware routing
This allows to dynamically increase routing metric on the IP subnets advertised from the Master SRRP node in comparison to the Standby SRRP node. It also allows to advertise and withdraw routes from a routing protocol based on the SRRP state. In this way, downstream traffic is routed in a predictable manner toward the active node (SRRP master state).
SRRP Fate Sharing for SRRP instances 10 and 11. This ensures congruency of SRRP states on the same node. This is a necessary step toward SRRP-aware routing.
Figure: IP subnet per SRRP master group