VPLS services support proxy-Address Resolution Protocol (proxy-ARP) and proxy-Neighbor Discovery (proxy-ND) functions cannot be enabled or disabled per service. When enabled, the config>service>system>evpn-proxy-arp-nd command populates the corresponding proxy-ARP or proxy-ND table with IP-to-MAC entries learned from the following sources:
EVPN-received IP-to-MAC entries
user-configured static IP-to-MAC entries
snooped dynamic IP-to-MAC entries (learned from ARP, GARP, or NA messages received on local SAPs; snooped dynamic IP-to-MAC entries on spoke-SDP bindings are not supported)
In addition, any ingress ARP or ND frame on a SAP are intercepted and processed. The system answers ARP requests and Neighbor Solicitation messages if the requested IP address is present in the proxy table.
The following figure shows an example proxy-ARP usage in an EVPN network. Proxy-ND functions in a similar way. The MAC address notation in the diagram is shortened for readability.
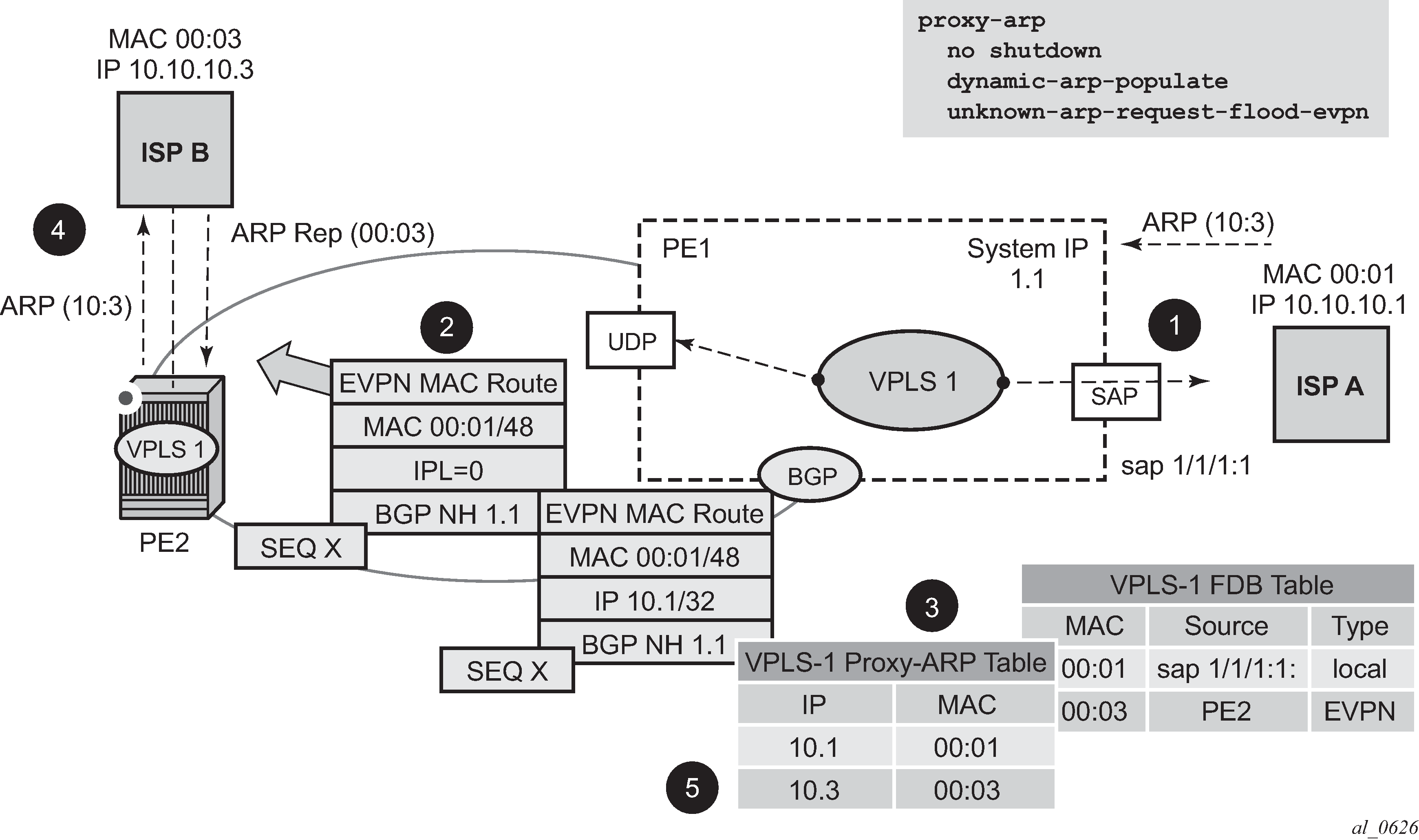
In the preceding figure, PE1 is configured as follows:
*A:Dut-B>config>service>system# info
----------------------------------------------
evpn-proxy-arp-nd
----------------------------------------------
*A:Dut-B>config>service>vpls# info
----------------------------------------------
description "Vpls 1 "
service-mtu 1400
split-horizon-group "vpls1" create
description "Default description for SHG vpls1"
exit
bgp
route-distinguisher auto-rd
route-target export target:100:1 import target:100:1
pw-template-binding 100
exit
exit
bgp-evpn
evi 1
mpls
split-horizon-group "vpls1"
ingress-replication-bum-label
auto-bind-tunnel
resolution-filter
ldp
exit
resolution filter
exit
no shutdown
exit
exit
stp
shutdown
exit
sap lag-1:1 create
description "Default sap description for service id 1"
no shutdown
exit
proxy-arp
age-time 600
send-refresh 200
dup-detect window 3 num-moves 3 hold-down max anti-spoof-
mac 00:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa
dynamic-arp-populate
no shutdown
exit
no shutdown
----------------------------------------------
*A:Dut-B>config>service>vpls#
The preceding figure shows the following steps, assuming proxy-ARP is no shutdown on PE1 and PE2, and the tables are empty:
ISP-A sends ARP-request for 10.10.10.3.
PE1 learns the MAC 00:01 in the FDB as usual and advertises it in EVPN without any IP. Optionally if the MAC is configured as a Cstatic MAC, it is advertised as a protected MAC to other PEs with the sticky bit set.
The ARP-request is sent to the CPM, where it is handled as follows:
An ARP entry (IP 10.1'MAC 00:01) is populated into the proxy-ARP table.
EVPN advertises MAC 00:01 and IP 10.1 in EVPN with the same SEQ number and protected bit as the previous route-type 2 for MAC 00:01.
A GARP is also issued to other SAPs/SDP-bindings (assuming they are not in the same split-horizon group as the source). If the garp-flood-evpn command is enabled, the GARP message is also sent to the EVPN network.
The original ARP-request can still be flooded to the EVPN or not based on the unknown-arp-request-flood-evpn command.
Assuming PE1 was configured with unknown-arp-request-flood-evpn, the ARP-request is flooded to PE2 and delivered to ISP-B. ISP-B replies with its MAC in the ARP-reply. The ARP-reply is finally delivered to ISP-A.
PE2 learns MAC 00:01 in the FDB and the entry 10.1'00:01 in the proxy-ARP table, based on the EVPN advertisements.
When ISP-B replies with its MAC in the ARP-reply, the MAC is handled as follows:
MAC 00:03 is learned in FDB at PE2 and advertised in EVPN.
MAC 00:03 and IP 10.3 are learned in the proxy-ARP table and advertised in EVPN with the same SEQ number as the previous MAC route.
ARP-reply is unicasted to MAC 00:01.
EVPN advertisements are used to populate PE1's FDB (MAC 00:03) and proxy-ARP (IP 10.3 to MAC 00:03) tables as mentioned in5.
From this point onward, the PEs reply to any ARP-request for 00:01 or 00:03 without the need for flooding the message in the EVPN network. By replying to known ARP-requests and Neighbor Solicitations, the PEs help to significantly reduce the flooding in the network.
Use the following commands to customize proxy-ARP/proxy-ND behavior:
dynamic-arp-populate and dynamic-nd-populate
These commands enable the addition of dynamic entries to the proxy-ARP or proxy-ND table (disabled by default). When executed, the system populates proxy-ARP/proxy-ND entries from snooped GARP/ARP/NA messages on SAPs/SDP-bindings, in addition to the entries coming from EVPN (if EVPN is enabled). These entries are shown as dynamic.
static ipv4-address mac-address, static ipv4-address mac-address, and static ipv6-address mac-address {host | router}
These commands configure static entries to be added to the table.
Note:A static IP-to-MAC entry requires the addition of the MAC address to the FDB as either learned or CStatic (conditional static mac) in order to become active (Status active).
age-time seconds
This command specifies the aging timer per proxy-ARP/proxy-ND entry. When the aging expires, the entry is flushed. The age is reset when a new ARP/GARP/NA for the same IP-to-MAC is received.
send-refresh seconds
If this command is enabled, the system sends ARP-request or Neighbor Solicitation (NS) messages at the configured time, which enables the owner of the IP to reply and, therefore, refresh its IP-to-MAC (proxy-ARP entry) and MAC (FDB entry).
table-size table-size
This command enables the user to limit the number of entries learned on a specified service. By default, the table-size limit is 250.
Flooding unknown ARP-requests, NS messages, or unsolicited GARPs and NA messages in an EVPN network can be configured using the following commands:
proxy-arp [no] unknown-arp-request-flood-evpn
proxy-arp [no] garp-flood-evpn
proxy-nd [no] unknown-ns-flood-evpn
proxy-nd [no] host-unsolicited-na-flood-evpn
proxy-nd [no] router-unsolicited-na-flood-evpn
dup-detect [anti-spoof-mac mac-address] window minutes num-moves count hold-down minutes | max
This command enables a mechanism that detects duplicate IPs and ARP/ND spoofing attacks. The following is a summary of the dup-detect command mechanism:
Attempts (relevant to dynamic and EVPN entry types) to add the same IP (different MAC) are monitored for window minutes value and when the count value is reached within the configured window, the proxy-ARP/proxy-ND entry for the IP is suspected and marked as duplicate. An alarm is also triggered.
The condition is cleared when hold-down time expires (max does not expire) or a clear command is issued.
If the anti-spoof-mac command is configured, the proxy-ARP or proxy-ND offending entry's MAC is replaced by the configured mac-address and advertised in an unsolicited GARP/NA for local SAP or SDP-bindings and in EVPN to remote PEs.
This mechanism assumes that the same anti-spoof-mac is configured in all PEs for the service, and that traffic with destination anti-spoof-mac received on SAPs/SDP-bindings is dropped. An ingress MAC filter must be configured to drop traffic to the anti-spoof-mac.
The following table shows the combinations that produce a Status = Active proxy-ARP entry in the table. The system only replies to proxy-ARP requests for active entries. Any other combination result in a Status = inActv entry. If the service is not active, the proxy-ARP entries are not active, regardless of the FDB entries
A static entry is active in the FDB even when the service is down.
Proxy-ARP entry type |
FDB entry type (for the same MAC) |
|---|---|
Dynamic |
learned |
Static |
CStatic |
EVPN |
EVPN, EVPNS with matching ESI |
Duplicate |
— |
When proxy-ARP or proxy-ND is enabled on services with multi-homed ESs, a proxy-ARP entry type ‟EVPN” might be associated with a ‟learned” FDB entry because the CE can send traffic for the same MAC to all the multi-homed PEs in the ES. In such cases, the entry is inactive, in accordance with the preceding table.