Gx is a reference point in the network architecture model describing mobile service delivery. The network elements are described in various technical documents under the umbrella of 3GPP and are used to deliver, manage, report on and charge end-user traffic for mobile users. The Gx reference point is used for policy control and charging control. As shown in Figure: Gx reference point, it is placed between a policy server (Policy and Rule Charging Function (PCRF)) and a traffic forwarding node (Policy and Charging Enforcement Function) that enforces rules set by the policy server.
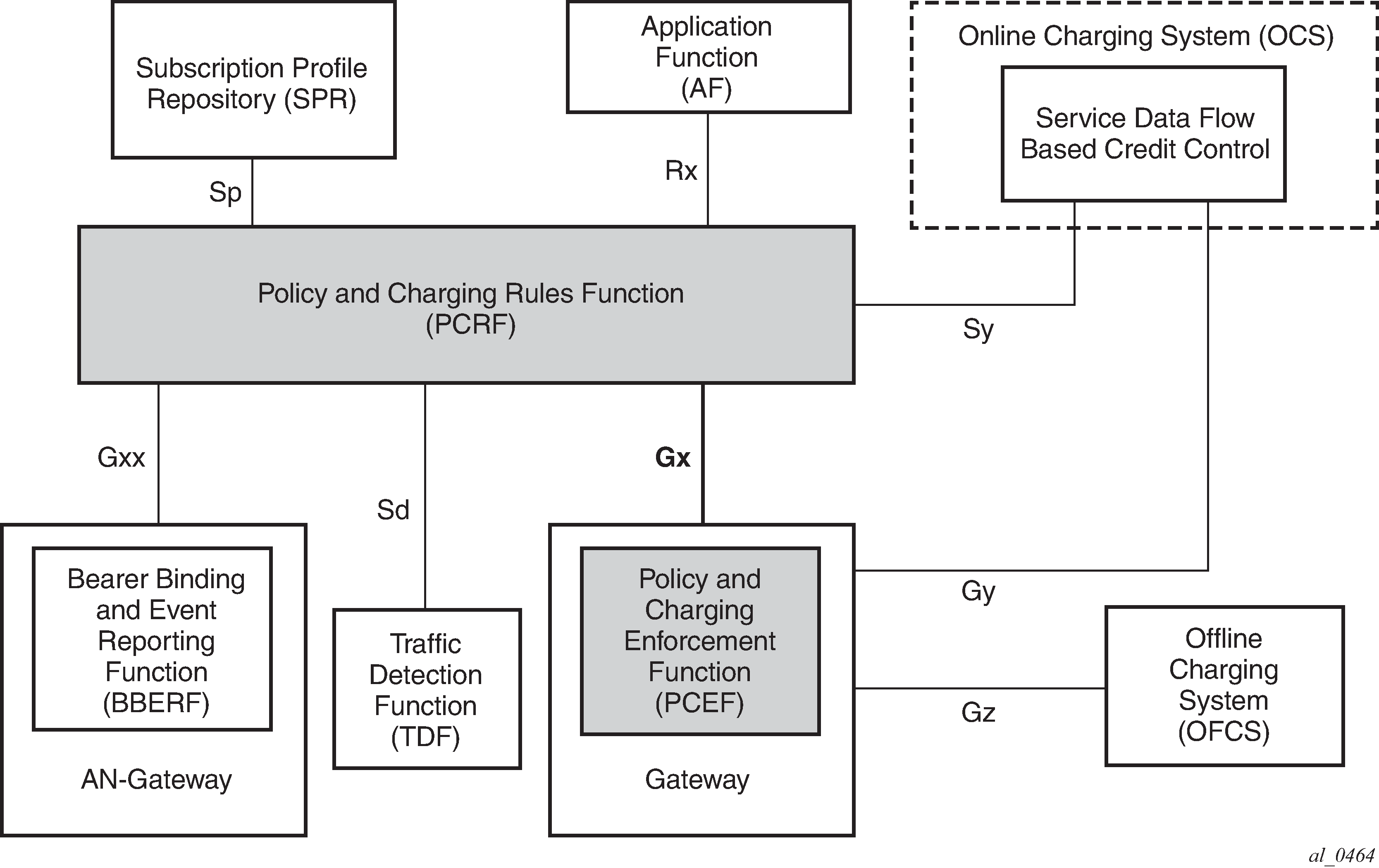
The Gx reference point is defined in the Policy and Charging Control (PCC) architecture within 3GPP standardization body. The PCC architecture is defined in the document 23.203 while the Gx functionality is defined in the document 29.212. Gx is an application of the Diameter protocol (RFC 3588/6733).
Although the Gx reference point is defined within 3GPP standardization body (spurred by mobile/wireless industry) its applicability has spread to wire-line operation as well. For example, mobile operators that also have fixed line customers (residential plus business) would like to streamline policy management in their mobile and non-mobile domains with a single and already existing Gx based policy management infrastructure. In other words they want to integrate policy management of nodes serving fixed line subscribers into the system that is currently managing mobile subscriber base.
In such mixed environments, the node plays the role of a PCEF with an integrated TDF (Traffic Detection Function, or Application Awareness [AA] in ALU terminology) where policies and charging rules can be managed via PCRF.
With Wi-Fi Offload as a new emerging application, supporting Gx reference point on nodes is becoming even more important.
The Gx interface on the node encompasses the following functionality:
Per subscriber host policy management
Usage-Monitoring
Gx is applicable to ESM as well as to AA.