Asymmetry removal is only supported on 7750 SR routed services. Asymmetry removal is a means of eliminating traffic asymmetry between a set of multi-homed SAP or spoke-sdp endpoints. This can be across endpoints within a single node or across a pair of inter-chassis link connected routers. Asymmetry means that the two directions of traffic for a flow (to-sub and from-sub) take different paths through the network. Asymmetry removal ensures that all packets for each flow, and all flows for each AA subscriber are diverted to an AA ISA.
Traffic asymmetry is created when there are multi-homed links for a service, and the links are simultaneously carrying traffic. In this scenario packets for flows use any reachable paths, therefore creating dynamic and changing asymmetry. Single node or multi-chassis asymmetry removal is used for any case where traffic for an AA subscriber may be forwarded over diverse paths on active AA divert links in a multi-homed topology. This includes support for SAP or spoke AA subscribers as well as business and residential transit AA subscribers within the diverted service.
Asymmetry removal must be implemented in the first routed hop on the network side of the subscriber management point, such that there is a deterministic and fixed SAP / spoke-SDP association between the downstream subscriber management the parent divert service.
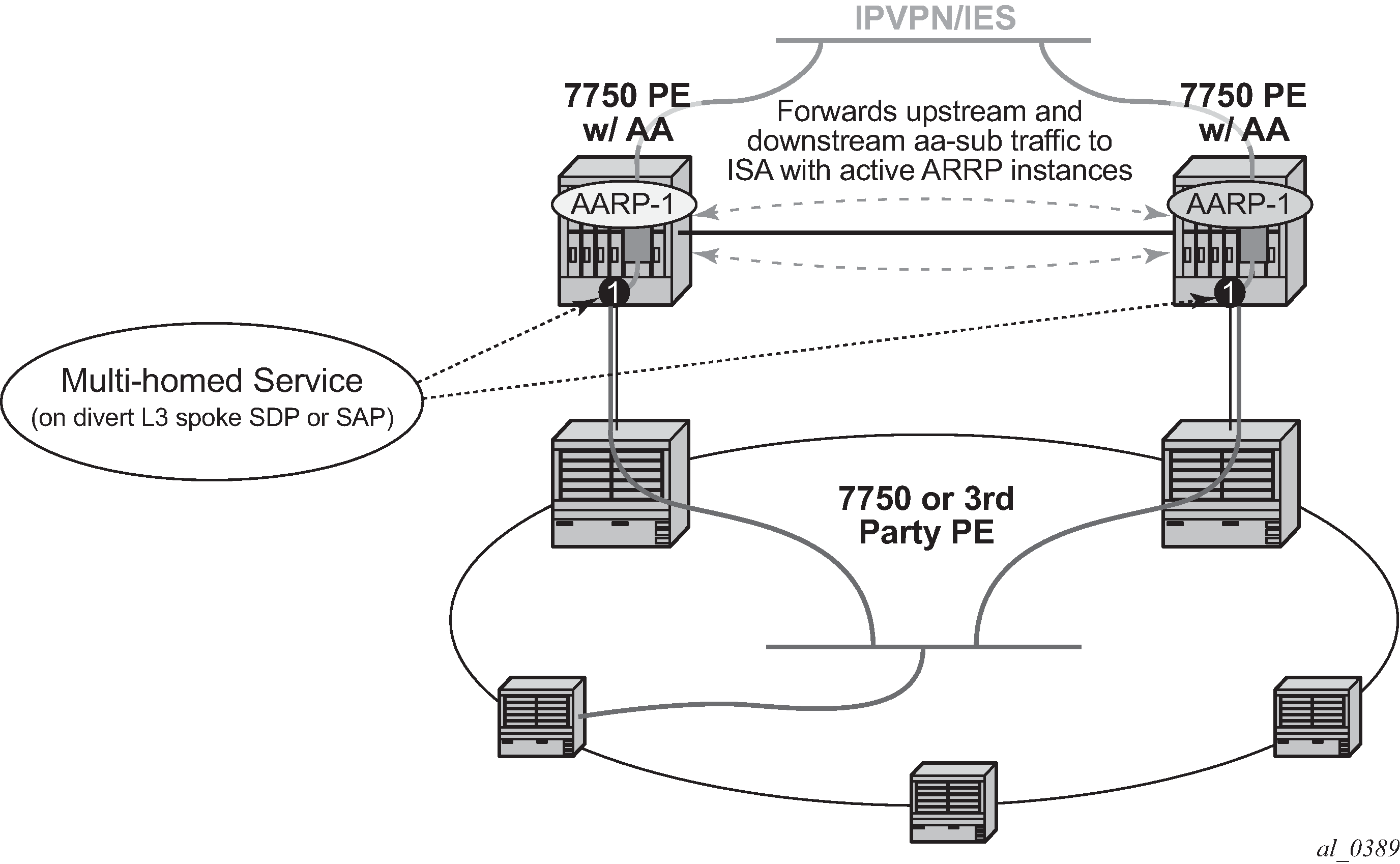
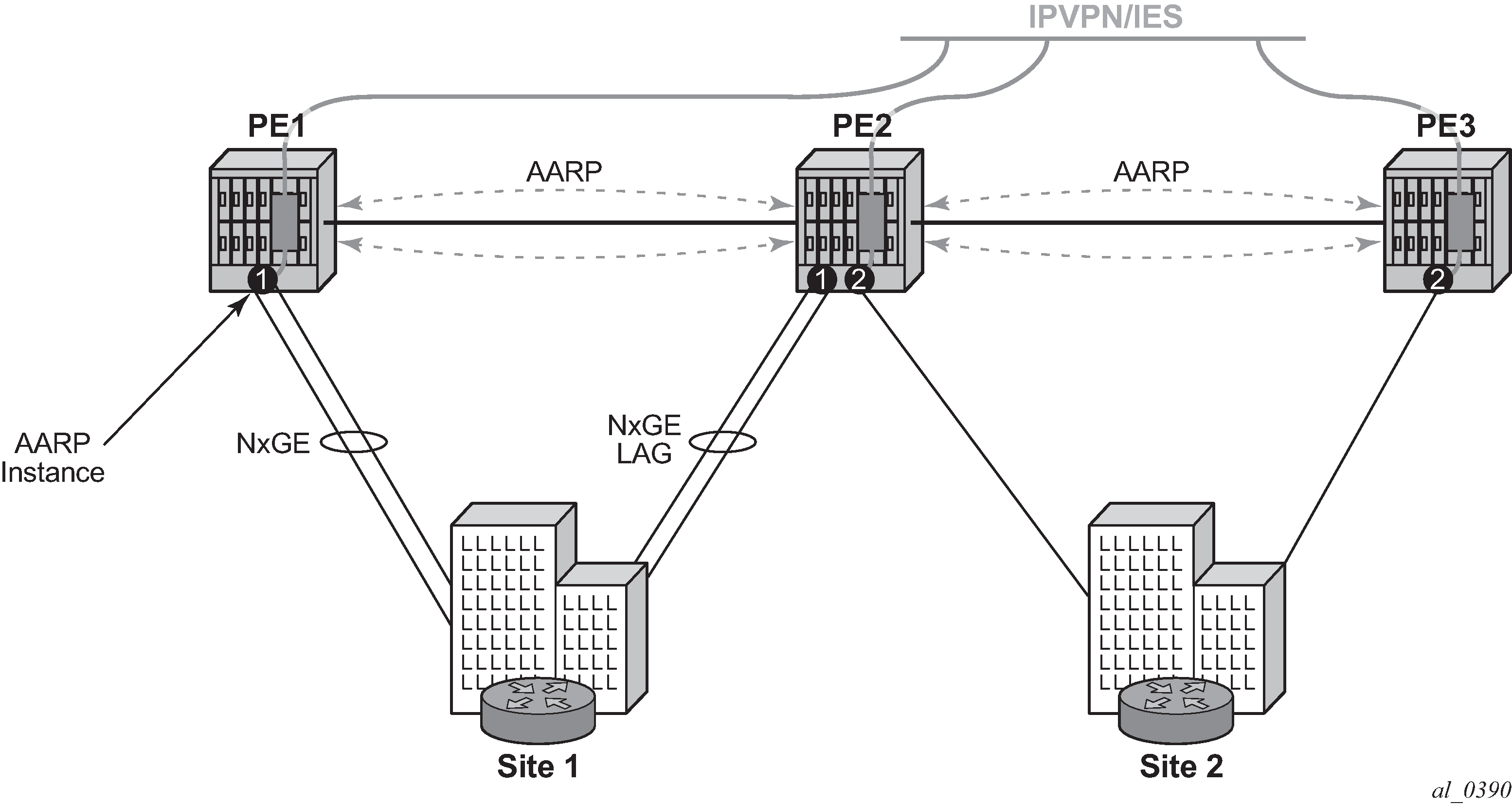
Asymmetry removal allows support for the SAP or spoke SDPs to the downstream element to be multi-homed on active links to redundant PE AA nodes as shown in Figure: Transit sub SAP and spoke SDP multi-homing with asymmetry.
AA for transit-ip subscribers is commonly deployed behind the point of the subscriber policy edge after aggregation. This includes cases where AA needed is behind:
any node running ESM but where there is no need or space to deploy distributed AA ISAs
legacy BRAS that do not support integrated application policy
Asymmetry removal also allows a VPN site (Figure: VPN site multi-homing with asymmetry ) to be connected with multi-homed, dual-active links while offering AA services with the ISA.
Asymmetry removal is supported for Layer 3 AA divert services:
IES SAP and spoke SDP
VPRN SAP and spoke SDP
When asymmetry exists between multi-chassis redundant systems, Ipipe spoke SDPs are used to interconnect these services between peer nodes over an Inter-Chassis Link (ICL).
Asymmetry removal supports multiple endpoints of a service with a common AARP instance, with a primary endpoint assigned the app-profile (and transit policy for transit subs). The remaining endpoints are defined as secondary endpoints of the AARP instance. All SAP or spoke endpoints within a specific AARP instance are load balanced to the same ISA in that node. Multi-endpoint AARP instances allow single-node asymmetry removal and multi-chassis asymmetry removal with multiple active links per node.