The other type of NGE domain is a private IP/MPLS network that traverses an intermediary network NGE domain; the intermediary network is used to interconnect nodes in the NGE domain using a multipoint-to-multipoint service. The intermediary network is typically a service provider network that provides a private IP VPN service or a private VPLS service used to interconnect a private network that does not mimic point-to-point links as described in the Private IP/MPLS network NGE domain section.
This type of NGE domain is shown in Figure: Private over intermediary network NGE domain.
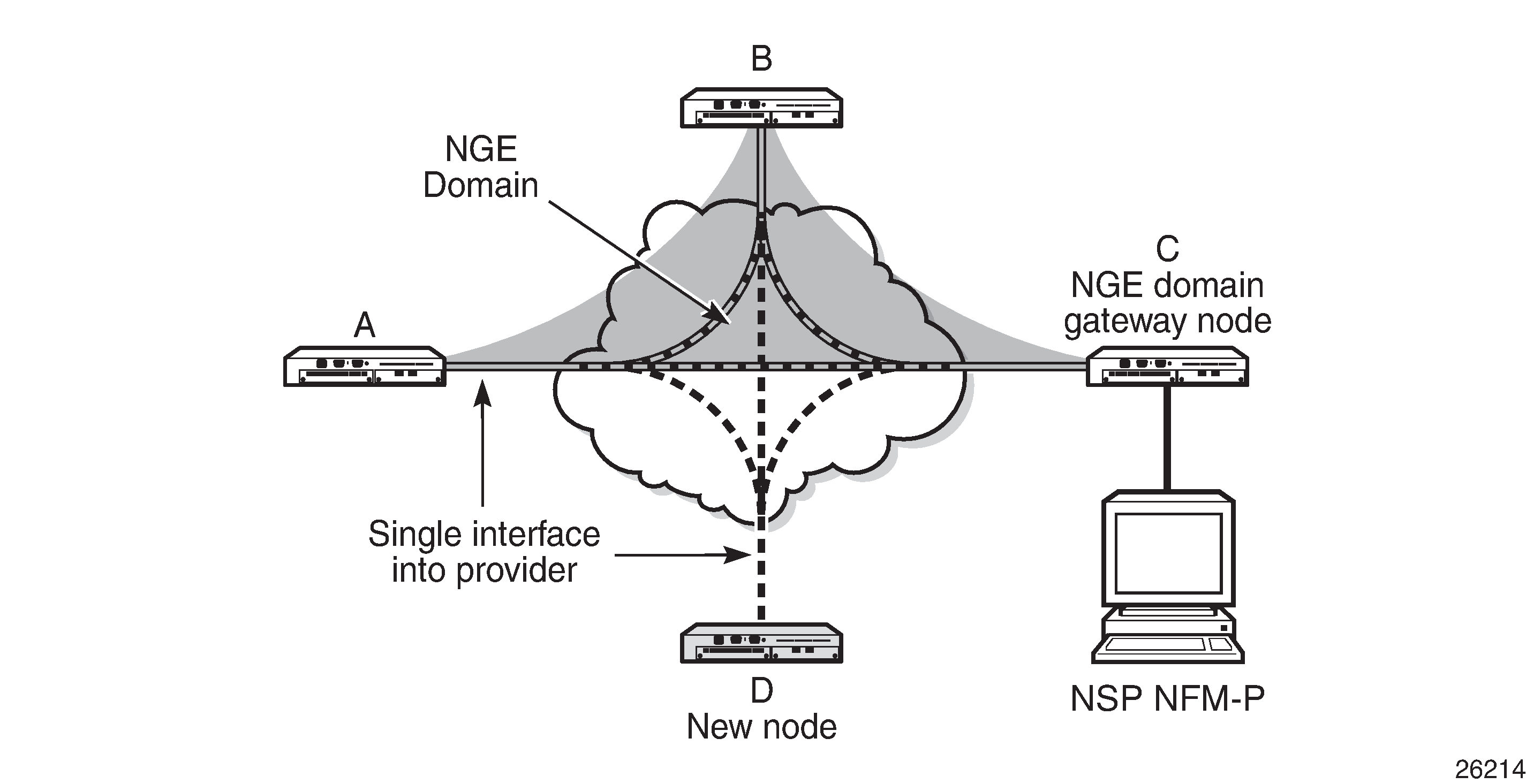
Private over intermediary network NGE domains have nodes with links that connect to a service provider network where a single link can communicate with multiple nodes over a Layer 3 service such as a VPRN. In Figure: Private over intermediary network NGE domain, node A has NGE enabled on its interface with the service provider and uses that single interface to communicate with nodes B and C, and eventually with node D when node D has been added to the NGE domain. This type of NGE domain requires the recognition of NGE gateway nodes that allow the NSP NFM-P to reach new nodes that enter the domain. Node C is designated as a gateway node.
When node D is added to the NGE domain, it must first have the NGE domain key group downloaded to it from the NSP NFM-P. The NSP NFM-P creates an NGE exception ACL on the gateway node, C, to allow communication with node D using SNMPv3 and SSH through the NGE domain. After the key group is downloaded, the NSP NFM-P enables router interface encryption on node D’s interface with the service provider and node D is now able to participate in the NGE domain. The NSP NFM-P automatically removes the IP exception ACL from node C when node D enters the NGE domain.
See Router interface NGE domain concepts for more information.