An NGE domain is a group of nodes and router interfaces forming a network that uses a single key group to create a security domain. NGE domains are created when router interface encryption is enabled on router interfaces that need to participate in the NGE domain. The NSP NFM-P assists operators in managing the nodes and interfaces that participate in the NGE domain. See the NSP NFM‑P User Guide for more information.
Figure: NGE Domain Transit shows various traffic types crossing an NGE domain.
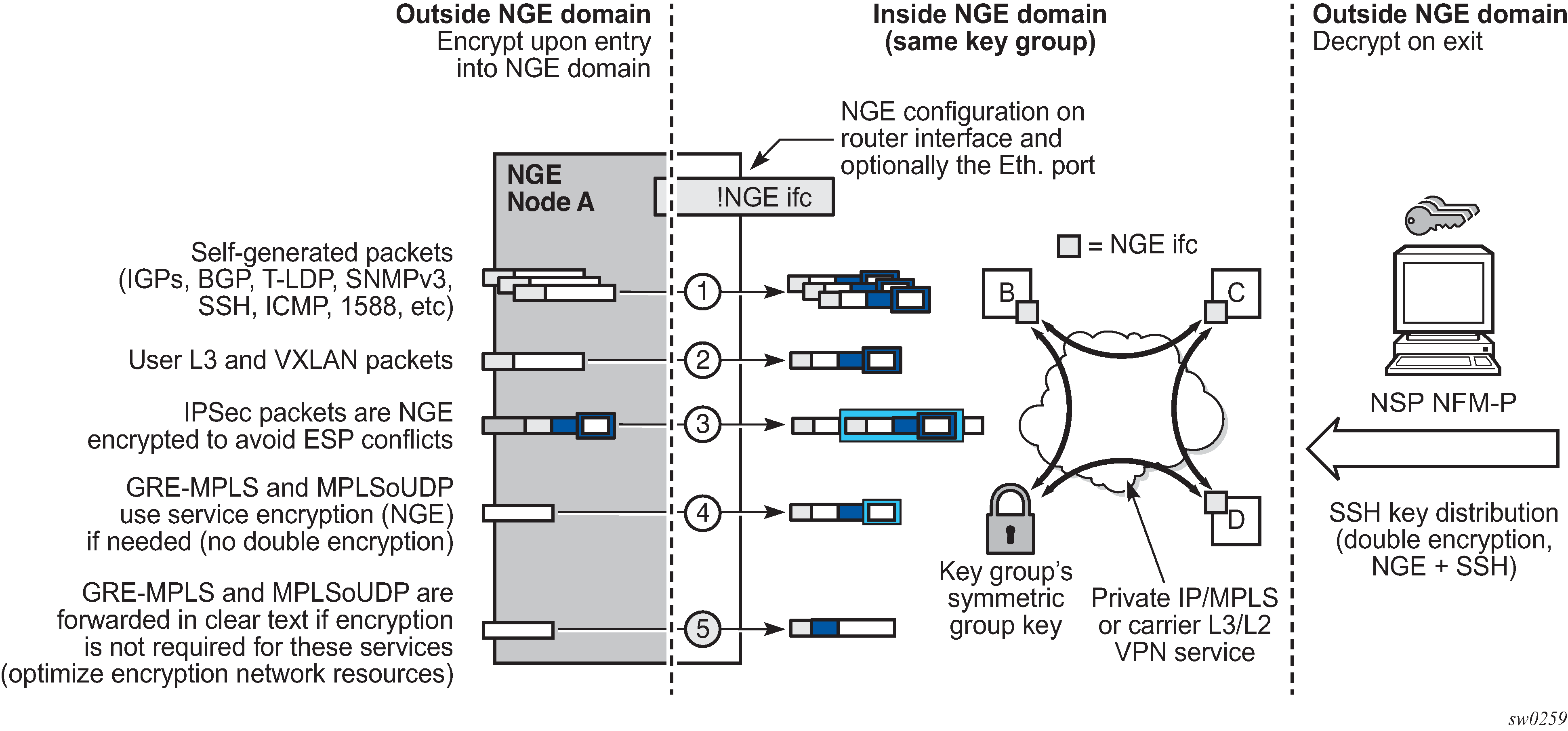
In Figure: NGE Domain Transit, nodes A, B, C, and D have router interfaces configured with router interface encryption enabled. Traffic is encrypted when entering the NGE domain using the key group configured on the router interface and is decrypted when exiting the NGE domain. Traffic may traverse multiple hops before exiting the NGE domain, yet decryption only occurs on the final node when the traffic exits the NGE domain.
Various traffic types are supported and encrypted when entering the NGE domain, as illustrated by the following items on node A in Figure: NGE Domain Transit:
Item 1: Self-generated packets
These packets, which include all types of control plane and management packets such as OSPF, BGP, LDP, SNMPv3, SSH, ICMP, RSVP-TE, and 1588, are encrypted.
Item 2: User Layer 3 and VXLAN packets
Any Layer 3 user packets that are routed into the NGE domain from an interface outside the NGE domain are encrypted. Any VXLAN packets that are routed into the NGE domain from this NGE node are encrypted.
Item 3: IPsec packets
IPsec packets are NGE-encrypted when entering the NGE domain to ensure that the IPsec packets’ security association information does not conflict with the NGE domain.
GRE-MPLS- or MPLSoUDP-based service traffic consists of Layer 3 packets, and router interface NGE is not applied to these types of packets. Instead, service-level NGE is used for encryption to avoid double-encrypting these packets and impacting throughput and latencies. The two types of GRE-MPLS or MPLSoUDP packets that can enter the NGE domain are illustrated by items 4 and 5 in Figure: NGE Domain Transit.
Item 4: GRE-MPLS and MPLSoUDP packets (SDP or VPRN) with service-level NGE enabled
These encrypted packets use the key group that is configured on the service. The services key group may be different from the key group configured on the router interface where the GRE-MPLS or MPLSoUDP packet enters the NGE domain.
Item 5: GRE-MPLS and MPLSoUDP packets (SDP or VPRN) with NGE disabled
These packets are not encrypted and can traverse the NGE domain in clear text. If these packets require encryption, SDP or VPRN encryption must be enabled.
Creating an NGE domain from the NSP NFM-P requires the operator to determine the type of NGE domain being managed. This indicates whether NGE gateway nodes are required to manage the NGE domain, and other operational considerations. The two types of NGE domains are: